 |
PDBsum entry 5tqs
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
PhospholipasE C gamma-1 c-terminal sh2 domain bound to a phosphopeptide derived from the receptor tyrosine kinase erbb2
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma-1. Chain: a, b, c, d. Fragment: unp residues 663-759. Synonym: plc-148,phosphoinositide phospholipasE C-gamma-1, phospholipasE C-ii,plc-ii,phospholipasE C-gamma-1,plc-gamma-1. Engineered: yes. Receptor protein-tyrosine kinase. Chain: e, f, h, g.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bos taurus. Bovine. Organism_taxid: 9913. Gene: plcg1. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Expression_system_cell_line: bl21(de3). Synthetic: yes. Homo sapiens.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.88Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.191
|
R-free:
|
0.237
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.S.Wuttke,M.A.Mckercher
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.A.McKercher
et al.
(2017).
Multimodal Recognition of Diverse Peptides by the C-Terminal SH2 Domain of Phospholipase C-γ1 Protein.
Biochemistry,
56,
2225-2237.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
24-Oct-16
|
Release date:
|
19-Apr-17
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P08487
(PLCG1_BOVIN) -
1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma-1 from Bos taurus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1291 a.a.
101 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 4 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.4.11
- phosphoinositide phospholipase C.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
myo-Inositol Phosphate Metabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate) + H2O = 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate + a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
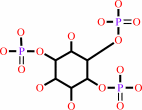 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
|
+
|
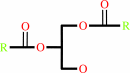 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
56:2225-2237
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Multimodal Recognition of Diverse Peptides by the C-Terminal SH2 Domain of Phospholipase C-γ1 Protein.
|
|
M.A.McKercher,
X.Guan,
Z.Tan,
D.S.Wuttke.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
SH2 domains recognize phosphotyrosine (pY)-containing peptide ligands and play
key roles in the regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase pathways. Each SH2
domain has individualized specificity, encoded in the amino acids neighboring
the pY, for defined targets that convey their distinct functions. The C-terminal
SH2 domain (PLCC) of the phospholipase C-γ1 full-length protein (PLCγ1)
typically binds peptides containing small and hydrophobic amino acids adjacent
to the pY, including a peptide derived from platelet-derived growth factor
receptor B (PDGFRB) and an intraprotein recognition site (Y783 of PLCγ1)
involved in the regulation of the protein's lipase activity. Remarkably, PLCC
also recognizes unexpected peptides containing amino acids with polar or bulky
side chains that deviate from this pattern. This versatility in recognition
specificity may allow PLCγ1 to participate in diverse, previously unrecognized,
signaling pathways in response to binding chemically dissimilar partners. We
have used structural approaches, including nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray
crystallography, to elucidate the mechanisms of noncognate peptide binding to
PLCC by ligands derived from receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB2 and from the insulin
receptor. The high-resolution peptide-bound structures reveal that PLCC has a
relatively static backbone but contains a chemically rich protein surface
comprised of a combination of hydrophobic pockets and amino acids with charged
side chains. We demonstrate that this expansive and chemically diverse PLCC
interface, in addition to peptide conformational plasticity, permits PLCC to
recognize specific noncognate peptide ligands with multimodal specificity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

