 |
PDBsum entry 5tk3
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.2.13
- fructose-bisphosphate aldolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate = D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
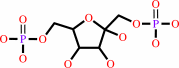 beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
|
=
|
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
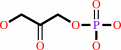 dihydroxyacetone phosphate
dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Biol Chem
292:19849-19860
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Isomer activation controls stereospecificity of class I fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolases.
|
|
P.W.Heron,
J.Sygusch.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) aldolase, a glycolytic enzyme, catalyzes the
reversible and stereospecific aldol addition of dihydroxyacetone phosphate
(DHAP) and d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (d-G3P) by an unresolved mechanism. To
afford insight into the molecular determinants of FBP aldolase stereospecificity
during aldol addition, a key ternary complex formed by DHAP and d-G3P,
comprising 2% of the equilibrium population at physiological pH, was cryotrapped
in the active site ofToxoplasma gondiialdolase crystals to high
resolution. The growth ofT. gondiialdolase crystals in acidic conditions
enabled trapping of the ternary complex as a dominant population. The obligate
3(S)-4(R) stereochemistry at the nascent C3-C4 bond of FBP
requires asi-face attack by the covalent DHAP nucleophile on the d-G3P
aldehydesi-face in the active site. Thecis-isomer of the d-G3P
aldehyde, representing the dominant population trapped in the ternary complex,
would lead tore-face attack on the aldehyde and yield tagatose
1,6-bisphosphate, a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme. We propose that
unhindered rotational isomerization by the d-G3P aldehyde moiety in the ternary
complex generates the activetrans-isomer competent for carbonyl bond
activation by active-site residues, thereby enablingsi-face attack by the
DHAP enamine. C-C bond formation by thecis-isomer is suppressed by
hydrogen bonding of thecis-aldehyde carbonyl with the DHAP enamine
phosphate dianion through a tetrahedrally coordinated water molecule. The active
site geometry further suppresses C-C bond formation with the l-G3P enantiomer of
d-G3P. Understanding C-C formation is of fundamental importance in biological
reactions and has considerable relevance to biosynthetic reactions in organic
chemistry.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

