 |
PDBsum entry 5o07
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
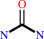 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem
32:1002-1011
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Insights into the binding mode of sulphamates and sulphamides to hCA II: crystallographic studies and binding free energy calculations.
|
|
G.De Simone,
E.Langella,
D.Esposito,
C.T.Supuran,
S.M.Monti,
J.Y.Winum,
V.Alterio.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Sulphamate and sulphamide derivatives have been largely investigated as carbonic
anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs) by means of different experimental techniques.
However, the structural determinants responsible for their different binding
mode to the enzyme active site were not clearly defined so far. In this paper,
we report the X-ray crystal structure of hCA II in complex with a sulphamate
inhibitor incorporating a nitroimidazole moiety. The comparison with the
structure of hCA II in complex with its sulphamide analogue revealed that the
two inhibitors adopt a completely different binding mode within the hCA II
active site. Starting from these results, we performed a theoretical study on
sulphamate and sulphamide derivatives, demonstrating that electrostatic
interactions with residues within the enzyme active site play a key role in
determining their binding conformation. These findings open new perspectives in
the design of effective CAIs using the sulphamate and sulphamide zinc binding
groups as lead compounds.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

