 |
PDBsum entry 5llh
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human carbonic anhydrase isozyme ii with 4-(1,3- benzothiazol-2-ylthio)-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzenesulfonamide
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Carbonic anhydrase 2. Chain: a. Fragment: human carbonic anhydrase ii. Synonym: carbonate dehydratase ii,carbonic anhydrasE C,cac,carbonic anhydrase ii,ca-ii. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: ca2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.90Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.188
|
R-free:
|
0.242
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
E.Manakova,A.Smirnov,S.Grazulis
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.Smirnov
et al.
(2018).
Crystal structure correlations with the intrinsic thermodynamics of human carbonic anhydrase inhibitor binding.
PeerJ,
6,
e4412.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-Jul-16
|
Release date:
|
16-Aug-17
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00918
(CAH2_HUMAN) -
Carbonic anhydrase 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
260 a.a.
257 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
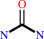 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
PeerJ
6:e4412
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure correlations with the intrinsic thermodynamics of human carbonic anhydrase inhibitor binding.
|
|
A.Smirnov,
A.Zubrienė,
E.Manakova,
S.Gražulis,
D.Matulis.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structure-thermodynamics correlation analysis was performed for a series of
fluorine- and chlorine-substituted benzenesulfonamide inhibitors binding to
several human carbonic anhydrase (CA) isoforms. The total of 24 crystal
structures of 16 inhibitors bound to isoforms CA I, CA II, CA XII, and CA XIII
provided the structural information of selective recognition between a compound
and CA isoform. The binding thermodynamics of all structures was determined by
the analysis of binding-linked protonation events, yielding the intrinsic
parameters, i.e., the enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs energy of binding. Inhibitor
binding was compared within structurally similar pairs that differ by
para- or meta-substituents enabling to obtain the contributing
energies of ligand fragments. The pairs were divided into two groups. First,
similar binders-the pairs that keep the same orientation of the benzene
ring exhibited classical hydrophobic effect, a less exothermic enthalpy and a
more favorable entropy upon addition of the hydrophobic fragments. Second,
dissimilar binders-the pairs of binders that demonstrated altered
positions of the benzene rings exhibited the non-classical hydrophobic effect, a
more favorable enthalpy and variable entropy contribution. A deeper
understanding of the energies contributing to the protein-ligand recognition
should lead toward the eventual goal of rational drug design where chemical
structures of ligands could be designed based on the target protein structure.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

