 |
PDBsum entry 5ivy

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5ivy
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Linked kdm5a jmj domain bound to the inhibitor n16 [3-(2-(4- chlorophenyl)acetamido)isonicotinic acid]
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Lysine-specific demethylase 5a. Chain: a. Fragment: linked kdm5a jmj domain, unp residues 1-87 and 348-588. Synonym: histone demethylase jarid1a,jumonji/arid domain-containing protein 1a,retinoblastoma-binding protein 2,rbbp-2. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: kdm5a, jarid1a, rbbp2, rbp2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Expression_system_variant: gold c-plus
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.45Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.187
|
R-free:
|
0.209
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.R.Horton,X.Cheng
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.R.Horton
et al.
(2016).
Structural Basis for KDM5A Histone Lysine Demethylase Inhibition by Diverse Compounds.
Cell Chem Biol,
23,
769-781.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
21-Mar-16
|
Release date:
|
27-Jul-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P29375
(KDM5A_HUMAN) -
Lysine-specific demethylase 5A from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1690 a.a.
300 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 61 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.67
- [histone H3]-trimethyl-L-lysine(4) demethylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6,N6,N6-trimethyl-L-lysyl4-[histone H3] + 3 2-oxoglutarate + 3 O2 = L-lysyl4-[histone H3] + 3 formaldehyde + 3 succinate + 3 CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6),N(6),N(6)-trimethyl-L-lysyl(4)-[histone H3]
|
+
|
 3
×
2-oxoglutarate
3
×
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
 3
×
O2
3
×
O2
|
=
|
L-lysyl(4)-[histone H3]
|
+
|
 3
×
formaldehyde
3
×
formaldehyde
|
+
|
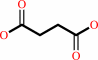 3
×
succinate
3
×
succinate
|
+
|
 3
×
CO2
3
×
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Cell Chem Biol
23:769-781
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural Basis for KDM5A Histone Lysine Demethylase Inhibition by Diverse Compounds.
|
|
J.R.Horton,
X.Liu,
M.Gale,
L.Wu,
J.R.Shanks,
X.Zhang,
P.J.Webber,
J.S.Bell,
S.C.Kales,
B.T.Mott,
G.Rai,
D.J.Jansen,
M.J.Henderson,
D.J.Urban,
M.D.Hall,
A.Simeonov,
D.J.Maloney,
M.A.Johns,
H.Fu,
A.Jadhav,
P.M.Vertino,
Q.Yan,
X.Cheng.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The KDM5/JARID1 family of Fe(II)- and α-ketoglutarate-dependent demethylases
removes methyl groups from methylated lysine 4 of histone H3. Accumulating
evidence supports a role for KDM5 family members as oncogenic drivers. We
compare the in vitro inhibitory properties and binding affinity of ten diverse
compounds with all four family members, and present the crystal structures of
the KDM5A-linked Jumonji domain in complex with eight of these inhibitors in the
presence of Mn(II). All eight inhibitors structurally examined occupy the
binding site of α-ketoglutarate, but differ in their specific binding
interactions, including the number of ligands involved in metal coordination. We
also observed inhibitor-induced conformational changes in KDM5A, particularly
those residues involved in the binding of α-ketoglutarate, the anticipated
peptide substrate, and intramolecular interactions. We discuss how particular
chemical moieties contribute to inhibitor potency and suggest strategies that
might be utilized in the successful design of selective and potent epigenetic
inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

