 |
PDBsum entry 5iv4
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.6.1.1
- adenylate cyclase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ATP = 3',5'-cyclic AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
3',5'-cyclic AMP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 48.15% similarity
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
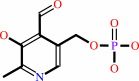 Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Chem Biol
12:838-844
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Discovery of LRE1 as a specific and allosteric inhibitor of soluble adenylyl cyclase.
|
|
L.Ramos-Espiritu,
S.Kleinboelting,
F.A.Navarrete,
A.Alvau,
P.E.Visconti,
F.Valsecchi,
A.Starkov,
G.Manfredi,
H.Buck,
C.Adura,
J.H.Zippin,
J.van den Heuvel,
J.F.Glickman,
C.Steegborn,
L.R.Levin,
J.Buck.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The prototypical second messenger cAMP regulates a wide variety of physiological
processes. It can simultaneously mediate diverse functions by acting locally in
independently regulated microdomains. In mammalian cells, two types of adenylyl
cyclase generate cAMP: G-protein-regulated transmembrane adenylyl cyclases and
bicarbonate-, calcium- and ATP-regulated soluble adenylyl cyclase (sAC). Because
each type of cyclase regulates distinct microdomains, methods to distinguish
between them are needed to understand cAMP signaling. We developed a
mass-spectrometry-based adenylyl cyclase assay, which we used to identify a new
sAC-specific inhibitor, LRE1. LRE1 bound to the bicarbonate activator binding
site and inhibited sAC via a unique allosteric mechanism. LRE1 prevented
sAC-dependent processes in cellular and physiological systems, and it will
facilitate exploration of the therapeutic potential of sAC inhibition.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

