 |
PDBsum entry 5hpy

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Gene regulation/signaling protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5hpy
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Gene regulation/signaling protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of rhoa.Gdp.Mgf3-in complex with human myosin 9b rhogap domain
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Unconventional myosin-ixb. Chain: a, d. Synonym: unconventional myosin-9b. Engineered: yes. Transforming protein rhoa. Chain: b, f. Fragment: unp residues 3-181. Synonym: rho cdna clone 12,h12. Engineered: yes.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: myo9b, myr5. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Gene: rhoa, arh12, arha, rho12.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.213
|
R-free:
|
0.246
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
F.S.Yi,J.Q.Ren,W.Feng
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
F.Yi
et al.
(2016).
Noncanonical Myo9b-RhoGAP Accelerates RhoA GTP Hydrolysis by a Dual-Arginine-Finger Mechanism.
J Mol Biol,
428,
3043-3057.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
21-Jan-16
|
Release date:
|
13-Jul-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, D:
E.C.?
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains B, F:
E.C.3.6.5.2
- small monomeric GTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
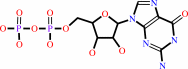
GTP + H2O = GDP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 GTP
GTP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
428:3043-3057
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Noncanonical Myo9b-RhoGAP Accelerates RhoA GTP Hydrolysis by a Dual-Arginine-Finger Mechanism.
|
|
F.Yi,
R.Kong,
J.Ren,
L.Zhu,
J.Lou,
J.Y.Wu,
W.Feng.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The GTP hydrolysis activities of Rho GTPases are stimulated by GTPase-activating
proteins (GAPs), which contain a RhoGAP domain equipped with a characteristic
arginine finger and an auxiliary asparagine for catalysis. However, the
auxiliary asparagine is missing in the RhoGAP domain of Myo9b (Myo9b-RhoGAP), a
unique motorized RhoGAP that specifically targets RhoA for controlling cell
motility. Here, we determined the structure of Myo9b-RhoGAP in complex with
GDP-bound RhoA and magnesium fluoride. Unexpectedly, Myo9b-RhoGAP contains two
arginine fingers at its catalytic site. The first arginine finger resembles the
one within the canonical RhoGAP domains and inserts into the nucleotide-binding
pocket of RhoA, whereas the second arginine finger anchors the Switch I loop of
RhoA and interacts with the nucleotide, stabilizing the transition state of GTP
hydrolysis and compensating for the lack of the asparagine. Mutating either of
the two arginine fingers impaired the catalytic activity of Myo9b-RhoGAP and
affected the Myo9b-mediated cell migration. Our data indicate that Myo9b-RhoGAP
accelerates RhoA GTP hydrolysis by a previously unknown dual-arginine-finger
mechanism, which may be shared by other noncanonical RhoGAP domains lacking the
auxiliary asparagine.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

