 |
PDBsum entry 5fpp
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of a pre-reaction ternary complex between sarin- acetylcholinesterase and hi-6
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Acetylcholinesterase. Chain: a, b. Fragment: catalytic domain, unp residues 32-574. Synonym: ache. Engineered: yes. Other_details: sarin phosphonylation product covalently attached to ser203
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mus musculus. House mouse. Organism_taxid: 10090. Expressed in: homo sapiens. Expression_system_taxid: 9606. Expression_system_cell_line: hek293f
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.176
|
R-free:
|
0.213
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Allgardsson,L.Berg,C.Akfur,A.Hornberg,F.Worek,A.Linusson,F.Ekstrom
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.Allgardsson
et al.
(2016).
Structure of a prereaction complex between the nerve agent sarin, its biological target acetylcholinesterase, and the antidote HI-6.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
113,
5514-5519.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
02-Dec-15
|
Release date:
|
11-May-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P21836
(ACES_MOUSE) -
Acetylcholinesterase from Mus musculus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
614 a.a.
541 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 5 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.7
- acetylcholinesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
acetylcholine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.18% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
choline
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 60.00% similarity
|
+
|
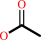 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
113:5514-5519
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of a prereaction complex between the nerve agent sarin, its biological target acetylcholinesterase, and the antidote HI-6.
|
|
A.Allgardsson,
L.Berg,
C.Akfur,
A.Hörnberg,
F.Worek,
A.Linusson,
F.J.Ekström.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Organophosphorus nerve agents interfere with cholinergic signaling by covalently
binding to the active site of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). This
inhibition causes an accumulation of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine,
potentially leading to overstimulation of the nervous system and death. Current
treatments include the use of antidotes that promote the release of functional
AChE by an unknown reactivation mechanism. We have used diffusion trap
cryocrystallography and density functional theory (DFT) calculations to
determine and analyze prereaction conformers of the nerve agent antidote HI-6 in
complex with Mus musculus AChE covalently inhibited by the nerve agent sarin.
These analyses reveal previously unknown conformations of the system and suggest
that the cleavage of the covalent enzyme-sarin bond is preceded by a
conformational change in the sarin adduct itself. Together with data from the
reactivation kinetics, this alternate conformation suggests a key interaction
between Glu202 and the O-isopropyl moiety of sarin. Moreover, solvent kinetic
isotope effect experiments using deuterium oxide reveal that the reactivation
mechanism features an isotope-sensitive step. These findings provide insights
into the reactivation mechanism and provide a starting point for the development
of improved antidotes. The work also illustrates how DFT calculations can guide
the interpretation, analysis, and validation of crystallographic data for
challenging reactive systems with complex conformational dynamics.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

