 |
PDBsum entry 5f1v

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase/lyase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5f1v
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.3.3.7
- 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + pyruvate = (2S,4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5- tetrahydrodipicolinate + H2O + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
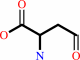 L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde
L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde
|
+
|
pyruvate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 71.43% similarity
|
=
|
(2S,4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5- tetrahydrodipicolinate
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
138:2014-2020
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Biomimetic Design Results in a Potent Allosteric Inhibitor of Dihydrodipicolinate Synthase from Campylobacter jejuni.
|
|
Y.V.Skovpen,
C.J.Conly,
D.A.Sanders,
D.R.Palmer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Dihydrodipicolinate synthase (DHDPS), an enzyme required for bacterial
peptidoglycan biosynthesis, catalyzes the condensation of pyruvate and
β-aspartate semialdehyde (ASA) to form a cyclic product which dehydrates to
form dihydrodipicolinate. DHDPS has, for several years, been considered a
putative target for novel antibiotics. We have designed the first potent
inhibitor of this enzyme by mimicking its natural allosteric regulation by
lysine, and obtained a crystal structure of the protein-inhibitor complex at 2.2
Å resolution. This novel inhibitor, which we named "bislysine",
resembles two lysine molecules linked by an ethylene bridge between the
α-carbon atoms. Bislysine is a mixed partial inhibitor with respect to the
first substrate, pyruvate, and a noncompetitive partial inhibitor with respect
to ASA, and binds to all forms of the enzyme with a Ki near 200 nM, more than
300 times more tightly than lysine. Hill plots show that the inhibition is
cooperative, indicating that the allosteric sites are not independent despite
being located on opposite sides of the protein tetramer, separated by
approximately 50 Å. A mutant enzyme resistant to lysine inhibition, Y110F, is
strongly inhibited by this novel inhibitor, suggesting this may be a promising
strategy for antibiotic development.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

