 |
PDBsum entry 5dcs

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5dcs
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.17.4.1
- ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-diphosphate + [thioredoxin]-disulfide + H2O = a ribonucleoside 5'-diphosphate + [thioredoxin]-dithiol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate
2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate
|
+
|
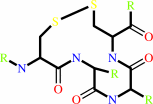 thioredoxin disulfide
thioredoxin disulfide
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
=
|
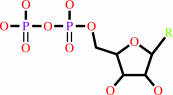 ribonucleoside diphosphate
ribonucleoside diphosphate
|
+
|
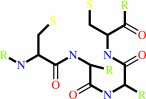 thioredoxin
thioredoxin
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(3+) or adenosylcob(III)alamin or Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Fe(3+)
|
or
|
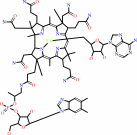 adenosylcob(III)alamin
adenosylcob(III)alamin
|
or
|
Mn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
290:25254-25272
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural Basis for Oxygen Activation at a Heterodinuclear Manganese/Iron Cofactor.
|
|
J.J.Griese,
R.Kositzki,
P.Schrapers,
R.M.Branca,
A.Nordström,
J.Lehtiö,
M.Haumann,
M.Högbom.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Two recently discovered groups of prokaryotic di-metal carboxylate proteins
harbor a heterodinuclear Mn/Fe cofactor. These are the class Ic ribonucleotide
reductase R2 proteins and a group of oxidases that are found predominantly in
pathogens and extremophiles, called R2-like ligand-binding oxidases (R2lox). We
have recently shown that the Mn/Fe cofactor of R2lox self-assembles from Mn(II)
and Fe(II) in vitro and catalyzes formation of a tyrosine-valine ether
cross-link in the protein scaffold (Griese, J. J., Roos, K., Cox, N., Shafaat,
H. S., Branca, R. M., Lehtiö, J., Gräslund, A., Lubitz, W., Siegbahn, P. E.,
and Högbom, M. (2013) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 17189-17194). Here, we
present a detailed structural analysis of R2lox in the nonactivated, reduced,
and oxidized resting Mn/Fe- and Fe/Fe-bound states, as well as the nonactivated
Mn/Mn-bound state. X-ray crystallography and x-ray absorption spectroscopy
demonstrate that the active site ligand configuration of R2lox is essentially
the same regardless of cofactor composition. Both the Mn/Fe and the diiron
cofactor activate oxygen and catalyze formation of the ether cross-link, whereas
the dimanganese cluster does not. The structures delineate likely routes for
gated oxygen and substrate access to the active site that are controlled by the
redox state of the cofactor. These results suggest that oxygen activation
proceeds via similar mechanisms at the Mn/Fe and Fe/Fe center and that R2lox
proteins might utilize either cofactor in vivo based on metal availability.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

