 |
PDBsum entry 5d1c
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of d233g-y306f hdac8 in complex with a tetrapeptide substrate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Histone deacetylase 8. Chain: a, b. Synonym: hd8. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Hdac8 fluor de lys tetrapeptide substrate. Chain: c, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: hdac8, hdacl1, cda07. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Synthetic: yes. Unidentified. Organism_taxid: 32644
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.42Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.147
|
R-free:
|
0.167
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.Decroos,N.H.Christianson,L.E.Gullett,C.M.Bowman,K.E.Christianson, M.A.Deardorff,D.W.Christianson
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.Decroos
et al.
(2015).
Biochemical and structural characterization of HDAC8 mutants associated with Cornelia de Lange syndrome spectrum disorders.
Biochemistry,
54,
6501-6513.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
04-Aug-15
|
Release date:
|
21-Oct-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9BY41
(HDAC8_HUMAN) -
Histone deacetylase 8 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
377 a.a.
364 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.98
- histone deacetylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-acetyl-L-lysyl-[histone] + H2O = L-lysyl-[histone] + acetate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-acetyl-L-lysyl-[histone]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
L-lysyl-[histone]
|
+
|
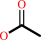 acetate
acetate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
54:6501-6513
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Biochemical and structural characterization of HDAC8 mutants associated with Cornelia de Lange syndrome spectrum disorders.
|
|
C.Decroos,
N.H.Christianson,
L.E.Gullett,
C.M.Bowman,
K.E.Christianson,
M.A.Deardorff,
D.W.Christianson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cornelia de Lange Syndrome (CdLS) spectrum disorders are characterized by
multiple organ system congenital anomalies that result from mutations in genes
encoding core cohesin proteins SMC1A, SMC3, and RAD21, or proteins that regulate
cohesin function such as NIPBL and HDAC8. HDAC8 is the Zn(2+)-dependent SMC3
deacetylase required for cohesin recycling during the cell cycle, and 17
different HDAC8 mutants have been identified to date in children diagnosed with
CdLS. As part of our continuing studies focusing on aberrant HDAC8 function in
CdLS, we now report the preparation and biophysical evaluation of five human
HDAC8 mutants: P91L, G117E, H180R, D233G, and G304R. Additionally, the double
mutants D233G-Y306F and P91L-Y306F were prepared to enable cocrystallization of
intact enzyme-substrate complexes. X-ray crystal structures of G117E,
P91L-Y306F, and D233G-Y306F HDAC8 mutants reveal that each CdLS mutation causes
structural changes that compromise catalysis and/or thermostability. For
example, the D233G mutation disrupts the D233-K202-S276 hydrogen bond network,
which stabilizes key tertiary structure interactions, thereby significantly
compromising thermostability. Molecular dynamics simulations of H180R and G304R
HDAC8 mutants suggest that the bulky arginine side chain of each mutant
protrudes into the substrate binding site and also causes active site residue
Y306 to fluctuate away from the position required for substrate activation and
catalysis. Significantly, the catalytic activities of most mutants can be
partially or fully rescued by the activator N-(phenylcarbamothioyl)-benzamide,
suggesting that HDAC8 activators may serve as possible leads in the therapeutic
management of CdLS.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

