 |
PDBsum entry 5cb8
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.25
- adenylyl-sulfate kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate + ATP = 3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
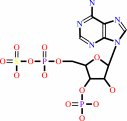 3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate
3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
290:24705-24714
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Recapitulating the Structural Evolution of Redox Regulation in Adenosine 5'-Phosphosulfate Kinase from Cyanobacteria to Plants.
|
|
J.Herrmann,
D.Nathin,
S.G.Lee,
T.Sun,
J.M.Jez.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In plants, adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS) kinase (APSK) is required for
reproductive viability and the production of 3'-phosphoadenosine
5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) as a sulfur donor in specialized metabolism. Previous
studies of the APSK from Arabidopsis thaliana (AtAPSK) identified a regulatory
disulfide bond formed between the N-terminal domain (NTD) and a cysteine on the
core scaffold. This thiol switch is unique to mosses, gymnosperms, and
angiosperms. To understand the structural evolution of redox control of APSK, we
investigated the redox-insensitive APSK from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis
sp. PCC 6803 (SynAPSK). Crystallographic analysis of SynAPSK in complex with
either APS and a non-hydrolyzable ATP analog or APS and sulfate revealed the
overall structure of the enzyme, which lacks the NTD found in homologs from
mosses and plants. A series of engineered SynAPSK variants reconstructed the
structural evolution of the plant APSK. Biochemical analyses of SynAPSK, SynAPSK
H23C mutant, SynAPSK fused to the AtAPSK NTD, and the fusion protein with the
H23C mutation showed that the addition of the NTD and cysteines recapitulated
thiol-based regulation. These results reveal the molecular basis for structural
changes leading to the evolution of redox control of APSK in the green lineage
from cyanobacteria to plants.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

