 |
PDBsum entry 5t6q

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5t6q
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.14.1
- unspecific monooxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an organic molecule + reduced [NADPH--hemoprotein reductase] + O2 = an alcohol + oxidized [NADPH--hemoprotein reductase] + H2O + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
organic molecule
|
+
|
reduced [NADPH--hemoprotein reductase]
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
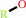 alcohol
alcohol
|
+
|
oxidized [NADPH--hemoprotein reductase]
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Heme-thiolate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
292:5610-5621
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The Crystal Structure of Cytochrome P450 4B1 (CYP4B1) Monooxygenase Complexed with Octane Discloses Several Structural Adaptations for ω-Hydroxylation.
|
|
M.H.Hsu,
B.R.Baer,
A.E.Rettie,
E.F.Johnson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
P450 family 4 fatty acid ω-hydroxylases preferentially oxygenate primary C-H
bonds over adjacent, energetically favored secondary C-H bonds, but the
mechanism explaining this intriguing preference is unclear. To this end, the
structure of rabbit P450 4B1 complexed with its substrate octane was determined
by X-ray crystallography to define features of the active site that contribute
to a preference for ω-hydroxylation. The structure indicated that octane is
bound in a narrow active-site cavity that limits access of the secondary C-H
bond to the reactive intermediate. A highly conserved sequence motif on helix I
contributes to positioning the terminal carbon of octane for ω-hydroxylation.
Glu-310 of this motif auto-catalytically forms an ester bond with the heme
5-methyl, and the immobilized Glu-310 contributes to substrate positioning. The
preference for ω-hydroxylation was decreased in an E310A mutant having a
shorter side chain, but the overall rates of metabolism were retained. E310D and
E310Q substitutions having longer side chains exhibit lower overall rates,
likely due to higher conformational entropy for these residues, but they
retained high preferences for octane ω-hydroxylation. Sequence comparisons
indicated that active-site residues constraining octane for ω-hydroxylation are
conserved in family 4 P450s. Moreover, the heme 7-propionate is positioned in
the active site and provides additional restraints on substrate binding. In
conclusion, P450 4B1 exhibits structural adaptations for ω-hydroxylation that
include changes in the conformation of the heme and changes in a highly
conserved helix I motif that is associated with selective oxygenation of
unactivated primary C-H bonds.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

