 |
PDBsum entry 5o5e
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human udp-n-acetylglucosamine-dolichyl-phosphate n-acetylglucosaminephosphotransferase (dpagt1) (v264g mutant) in complex with tunicamycin
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Udp-n-acetylglucosamine--dolichyl-phosphate n- acetylglucosaminephosphotransferase. Chain: a. Synonym: glcnac-1-p transferase,gpt,n-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: dpagt1, dpagt2. Expressed in: spodoptera frugiperda. Expression_system_taxid: 7108.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.230
|
R-free:
|
0.236
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.C.W.Pike,Y.Y.Dong,A.Chu,A.Tessitore,S.Goubin,L.Dong,S.Mukhopadhyay, P.Mahajan,R.Chalk,G.Berridge,D.Wang,K.Kupinska,K.Belaya,D.Beeson, N.Burgess-Brown,A.M.Edwards,C.H.Arrowsmith,C.Bountra,E.P.Carpenter, Structural Genomics Consortium (Sgc)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Y.Y.Dong
et al.
(2018).
Structures of DPAGT1 Explain Glycosylation Disease Mechanisms and Advance TB Antibiotic Design.
Cell,
175,
1045.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
01-Jun-17
|
Release date:
|
28-Feb-18
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9H3H5
(GPT_HUMAN) -
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine--dolichyl-phosphate N-acetylglucosaminephosphotransferase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
408 a.a.
381 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.8.15
- UDP-N-acetylglucosamine--dolichyl-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a di-trans,poly-cis-dolichyl phosphate + UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine = an N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-diphospho-di-trans,poly-cis-dolichol + UMP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
di-trans,poly-cis-dolichyl phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 43.59% similarity
|
+
|
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine
|
=
|
N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-diphospho-di-trans,poly-cis-dolichol
|
+
|
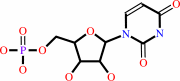 UMP
UMP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Cell
175:1045
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structures of DPAGT1 Explain Glycosylation Disease Mechanisms and Advance TB Antibiotic Design.
|
|
Y.Y.Dong,
H.Wang,
A.C.W.Pike,
S.A.Cochrane,
S.Hamedzadeh,
F.J.Wyszyński,
S.R.Bushell,
S.F.Royer,
D.A.Widdick,
A.Sajid,
H.I.Boshoff,
Y.Park,
R.Lucas,
W.M.Liu,
S.S.Lee,
T.Machida,
L.Minall,
S.Mehmood,
K.Belaya,
W.W.Liu,
A.Chu,
L.Shrestha,
S.M.M.Mukhopadhyay,
C.Strain-Damerell,
R.Chalk,
N.A.Burgess-Brown,
M.J.Bibb,
C.E.Barry Iii,
C.V.Robinson,
D.Beeson,
B.G.Davis,
E.P.Carpenter.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Protein N-glycosylation is a widespread post-translational modification. The
first committed step in this process is catalysed by
dolichyl-phosphate N-acetylglucosamine-phosphotransferase DPAGT1 (GPT/E.C.
2.7.8.15). Missense DPAGT1 variants cause congenital myasthenic syndrome and
disorders of glycosylation. In addition, naturally-occurring bactericidal
nucleoside analogues such as tunicamycin are toxic to eukaryotes due to DPAGT1
inhibition, preventing their clinical use. Our structures of DPAGT1 with the
substrate UDP-GlcNAc and tunicamycin reveal substrate binding modes, suggest a
mechanism of catalysis, provide an understanding of how mutations modulate
activity (thus causing disease) and allow design of non-toxic
"lipid-altered" tunicamycins. The structure-tuned activity of these
analogues against several bacterial targets allowed the design of potent
antibiotics for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, enabling treatment in vitro, in
cellulo and in vivo, providing a promising new class of antimicrobial drug.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

