 |
PDBsum entry 5ls7

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 25 a.a.
25 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 128 a.a.
128 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 102 a.a.
102 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Complex of wild type e. Coli alpha aspartate decarboxylase with its processing factor panz
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aspartate 1-decarboxylase. Chain: a. Synonym: aspartate alpha-decarboxylase. Engineered: yes. Other_details: residues 1-17 are the purification tag.. Pand maturation factor. Chain: b. Engineered: yes. Other_details: thE C-terminus is not visible in the electron density.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli k-12. Organism_taxid: 83333. Gene: pand, b0131, jw0127. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Gene: panm, panz, yhhk, b3459, jw3424. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.16Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.115
|
R-free:
|
0.137
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.C.F.Monteiro,M.E.Webb,A.R.Pearson
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Z.L.P.Arnott
et al.
(2017).
The Mechanism of Regulation of Pantothenate Biosynthesis by the PanD-PanZ·AcCoA Complex Reveals an Additional Mode of Action for the Antimetabolite N-Pentyl Pantothenamide (N5-Pan).
Biochemistry,
56,
4931-4939.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Aug-16
|
Release date:
|
13-Sep-17
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0A790
(PAND_ECOLI) -
Aspartate 1-decarboxylase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
126 a.a.
25 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, D:
E.C.4.1.1.11
- aspartate 1-decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Coenzyme A Biosynthesis (early stages)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-aspartate + H+ = beta-alanine + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
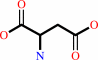 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
beta-alanine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 71.43% similarity
|
+
|
CO2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Pyruvate
Pyruvate
|
|
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chain B:
E.C.?
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
56:4931-4939
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The Mechanism of Regulation of Pantothenate Biosynthesis by the PanD-PanZ·AcCoA Complex Reveals an Additional Mode of Action for the Antimetabolite N-Pentyl Pantothenamide (N5-Pan).
|
|
Z.L.P.Arnott,
S.Nozaki,
D.C.F.Monteiro,
H.E.Morgan,
A.R.Pearson,
H.Niki,
M.E.Webb.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The antimetabolite pentyl pantothenamide has broad spectrum antibiotic activity
but exhibits enhanced activity against Escherichia coli. The PanDZ complex has
been proposed to regulate the pantothenate biosynthetic pathway in E. coli by
limiting the supply of β-alanine in response to coenzyme A concentration. We
show that formation of such a complex between activated aspartate decarboxylase
(PanD) and PanZ leads to sequestration of the pyruvoyl cofactor as a ketone
hydrate and demonstrate that both PanZ overexpression-linked β-alanine
auxotrophy and pentyl pantothenamide toxicity are due to formation of this
complex. This both demonstrates that the PanDZ complex regulates pantothenate
biosynthesis in a cellular context and validates the complex as a target for
antibiotic development.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |

