 |
PDBsum entry 5fdq

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5fdq
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase/inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Murine cox-2 s530t mutant
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Prostaglandin g/h synthase 2. Chain: a, b. Synonym: cyclooxygenase-2,cox-2,glucocorticoid-regulated inflammatory cyclooxygenase,gripghs,macrophage activation-associated marker protein p71/73,pes-2,phs ii,prostaglandin h2 synthase 2,pghs-2, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2,tis10 protein. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mus musculus. Mouse. Organism_taxid: 10090. Gene: ptgs2, cox-2, cox2, pghs-b, tis10. Expressed in: spodoptera frugiperda. Expression_system_taxid: 7108
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.90Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.155
|
R-free:
|
0.191
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.J.Lucido,B.J.Orlando,M.G.Malkowski
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.J.Lucido
et al.
(2016).
Crystal Structure of Aspirin-Acetylated Human Cyclooxygenase-2: Insight into the Formation of Products with Reversed Stereochemistry.
Biochemistry,
55,
1226-1238.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
16-Dec-15
|
Release date:
|
16-Mar-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q05769
(PGH2_MOUSE) -
Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 from Mus musculus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
604 a.a.
551 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 3 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.99.1
- prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoate + AH2 + 2 O2 = prostaglandin H2 + A + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoate
|
+
|
AH2
|
+
|
 2
×
O2
2
×
O2
|
=
|
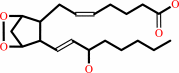 prostaglandin H2
prostaglandin H2
|
+
|
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 51.11% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
55:1226-1238
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal Structure of Aspirin-Acetylated Human Cyclooxygenase-2: Insight into the Formation of Products with Reversed Stereochemistry.
|
|
M.J.Lucido,
B.J.Orlando,
A.J.Vecchio,
M.G.Malkowski.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs target the cyclooxygenase
enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2) to block the formation of prostaglandins. Aspirin is
unique in that it covalently modifies each enzyme by acetylating Ser-530 within
the cyclooxygenase active site. Acetylation of COX-1 leads to complete loss of
activity, while acetylation of COX-2 results in the generation of the
monooxygenated product 15(R)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15R-HETE). Ser-530
has also been shown to influence the stereochemistry for the addition of oxygen
to the prostaglandin product. We determined the crystal structures of S530T
murine (mu) COX-2, aspirin-acetylated human (hu) COX-2, and huCOX-2 in complex
with salicylate to 1.9, 2.0, and 2.4 Å, respectively. The structures reveal
that (1) the acetylated Ser-530 completely blocks access to the hydrophobic
groove, (2) the observed binding pose of salicylate is reflective of the
enzyme-inhibitor complex prior to acetylation, and (3) the observed Thr-530
rotamer in the S530T muCOX-2 crystal structure does not impede access to the
hydrophobic groove. On the basis of these structural observations, along with
functional analysis of the S530T/G533V double mutant, we propose a working
hypothesis for the generation of 15R-HETE by aspirin-acetylated COX-2. We also
observe differential acetylation of COX-2 purified in various detergent systems
and nanodiscs, indicating that detergent and lipid binding within the
membrane-binding domain of the enzyme alters the rate of the acetylation
reaction in vitro.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

