 |
PDBsum entry 5e6h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5e6h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
A linked jumonji domain of the kdm5a lysine demethylase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Lysine-specific demethylase 5a. Chain: a. Synonym: histone demethylase jarid1a,jumonji/arid domain-containing protein 1a,retinoblastoma-binding protein 2,rbbp-2,histone demethylase jarid1a,jumonji/arid domain-containing protein 1a, retinoblastoma-binding protein 2,rbbp-2. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: kdm5a, jarid1a, rbbp2, rbp2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Expression_system_variant: gold/c-plus
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.24Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.181
|
R-free:
|
0.220
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.R.Horton,X.Cheng
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.R.Horton
et al.
(2016).
Characterization of a Linked Jumonji Domain of the KDM5/JARID1 Family of Histone H3 Lysine 4 Demethylases.
J Biol Chem,
291,
2631-2646.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
09-Oct-15
|
Release date:
|
16-Dec-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P29375
(KDM5A_HUMAN) -
Lysine-specific demethylase 5A from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1690 a.a.
294 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 62 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.67
- [histone H3]-trimethyl-L-lysine(4) demethylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6,N6,N6-trimethyl-L-lysyl4-[histone H3] + 3 2-oxoglutarate + 3 O2 = L-lysyl4-[histone H3] + 3 formaldehyde + 3 succinate + 3 CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6),N(6),N(6)-trimethyl-L-lysyl(4)-[histone H3]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 3
×
2-oxoglutarate
3
×
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
 3
×
O2
3
×
O2
|
=
|
L-lysyl(4)-[histone H3]
|
+
|
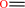 3
×
formaldehyde
3
×
formaldehyde
|
+
|
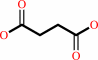 3
×
succinate
3
×
succinate
|
+
|
 3
×
CO2
3
×
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
291:2631-2646
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Characterization of a Linked Jumonji Domain of the KDM5/JARID1 Family of Histone H3 Lysine 4 Demethylases.
|
|
J.R.Horton,
A.Engstrom,
E.L.Zoeller,
X.Liu,
J.R.Shanks,
X.Zhang,
M.A.Johns,
P.M.Vertino,
H.Fu,
X.Cheng.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The KDM5/JARID1 family of Fe(II)- and α-ketoglutarate-dependent demethylases
remove methyl groups from tri- and dimethylated lysine 4 of histone H3.
Accumulating evidence from primary tumors and model systems supports a role for
KDM5A (JARID1A/RBP2) and KDM5B (JARID1B/PLU1) as oncogenic drivers. The KDM5
family is unique among the Jumonji domain-containing histone demethylases in
that there is an atypical insertion of a DNA-binding ARID domain and a
histone-binding PHD domain into the Jumonji domain, which separates the
catalytic domain into two fragments (JmjN and JmjC). Here we demonstrate that
internal deletion of the ARID and PHD1 domains has a negligible effect on in
vitro enzymatic kinetics of the KDM5 family of enzymes. We present a crystal
structure of the linked JmjN-JmjC domain from KDM5A, which reveals that the
linked domain fully reconstitutes the cofactor (metal ion and α-ketoglutarate)
binding characteristics of other structurally characterized Jumonji domain
demethylases. Docking studies with GSK-J1, a selective inhibitor of the
KDM6/KDM5 subfamilies, identify critical residues for binding of the inhibitor
to the reconstituted KDM5 Jumonji domain. Further, we found that GSK-J1
inhibited the demethylase activity of KDM5C with 8.5-fold increased potency
compared with that of KDM5B at 1 mm α-ketoglutarate. In contrast, JIB-04 (a
pan-inhibitor of the Jumonji demethylase superfamily) had the opposite effect
and was ∼8-fold more potent against KDM5B than against KDM5C. Interestingly,
the relative selectivity of JIB-04 toward KDM5B over KDM5C in vitro translates
to a ∼10-50-fold greater growth-inhibitory activity against breast cancer cell
lines. These data define the minimal requirements for enzymatic activity of the
KDM5 family to be the linked JmjN-JmjC domain coupled with the immediate
C-terminal helical zinc-binding domain and provide structural characterization
of the linked JmjN-JmjC domain for the KDM5 family, which should prove useful in
the design of KDM5 demethylase inhibitors with improved potency and selectivity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

