 |
PDBsum entry 5e65
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.3.1.1.53
- sialate O-acetylesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminate + H2O = N-acetylneuraminate + acetate + H+
|
|
2.
|
N-acetyl-4-O-acetylneuraminate + H2O = N-acetylneuraminate + acetate + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminate
N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminate
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 95.83% similarity
|
=
|
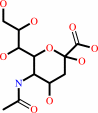 N-acetylneuraminate
N-acetylneuraminate
|
+
|
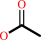 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
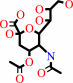 N-acetyl-4-O-acetylneuraminate
N-acetyl-4-O-acetylneuraminate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 N-acetylneuraminate
N-acetylneuraminate
|
+
|
 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 83.33% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
PLoS Pathog
12:e1005411
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
An Open Receptor-Binding Cavity of Hemagglutinin-Esterase-Fusion Glycoprotein from Newly-Identified Influenza D Virus: Basis for Its Broad Cell Tropism.
|
|
H.Song,
J.Qi,
Z.Khedri,
S.Diaz,
H.Yu,
X.Chen,
A.Varki,
Y.Shi,
G.F.Gao.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Influenza viruses cause seasonal flu each year and pandemics or epidemic
sporadically, posing a major threat to public health. Recently, a new influenza
D virus (IDV) was isolated from pigs and cattle. Here, we reveal that the IDV
utilizes 9-O-acetylated sialic acids as its receptor for virus entry. Then, we
determined the crystal structures of hemagglutinin-esterase-fusion glycoprotein
(HEF) of IDV both in its free form and in complex with the receptor and
enzymatic substrate analogs. The IDV HEF shows an extremely similar structural
fold as the human-infecting influenza C virus (ICV) HEF. However, IDV HEF has an
open receptor-binding cavity to accommodate diverse extended glycan moieties.
This structural difference provides an explanation for the phenomenon that the
IDV has a broad cell tropism. As IDV HEF is structurally and functionally
similar to ICV HEF, our findings highlight the potential threat of the virus to
public health.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

