 |
PDBsum entry 5e4n
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.54
- 3-deoxy-7-phosphoheptulonate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Shikimate and Chorismate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-erythrose 4-phosphate + phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O = 7-phospho-2- dehydro-3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptonate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
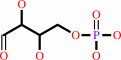 D-erythrose 4-phosphate
D-erythrose 4-phosphate
|
+
|
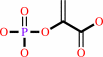 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
7-phospho-2- dehydro-3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptonate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Plos One
11:e0152723
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Probing the Sophisticated Synergistic Allosteric Regulation of Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Using ᴅ-Amino Acids.
|
|
S.Reichau,
N.J.Blackmore,
W.Jiao,
E.J.Parker.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Chirality plays a major role in recognition and interaction of biologically
important molecules. The enzyme 3-deoxy-d-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate
synthase (DAH7PS) is the first enzyme of the shikimate pathway, which is
responsible for the synthesis of aromatic amino acids in bacteria and plants,
and a potential target for the development of antibiotics and herbicides. DAH7PS
from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MtuDAH7PS) displays an unprecedented complexity
of allosteric regulation, with three interdependent allosteric binding sites and
a ternary allosteric response to combinations of the aromatic amino acids l-Trp,
l-Phe and l-Tyr. In order to further investigate the intricacies of this system
and identify key residues in the allosteric network of MtuDAH7PS, we studied the
interaction of MtuDAH7PS with aromatic amino acids that bear the non-natural
d-configuration, and showed that the d-amino acids do not elicit an allosteric
response. We investigated the binding mode of d-amino acids using X-ray
crystallography, site directed mutagenesis and isothermal titration calorimetry.
Key differences in the binding mode were identified: in the Phe site, a hydrogen
bond between the amino group of the allosteric ligands to the side chain of
Asn175 is not established due to the inverted configuration of the ligands. In
the Trp site, d-Trp forms no interaction with the main chain carbonyl group of
Thr240 and less favourable interactions with Asn237 when compared to the l-Trp
binding mode. Investigation of the MtuDAH7PSN175A variant further supports the
hypothesis that the lack of key interactions in the binding mode of the aromatic
d-amino acids are responsible for the absence of an allosteric response, which
gives further insight into which residues of MtuDAH7PS play a key role in the
transduction of the allosteric signal.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

