 |
PDBsum entry 5dz2
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Geosmin synthase from streptomyces coelicolor n-terminal domain complexed with three mg2+ ions and alendronic acid
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Germacradienol/geosmin synthase. Chain: a, b. Fragment: n-terminal domain (unp residues 1-338). Synonym: scgs. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Streptomyces coelicolor (strain atcc baa-471 / a3(2) / m145). Organism_taxid: 100226. Strain: atcc baa-471 / a3(2) / m145. Gene: cyc2, sco6073, sc9b1.20. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.11Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.210
|
R-free:
|
0.250
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
G.G.Harris,P.M.Lombardi,T.A.Pemberton,T.Matsui,T.M.Weiss,K.E.Cole, M.Koksal,F.V.Murphy,L.S.Vedula,W.K.W.Chou,D.E.Cane,D.W.Christianson
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
G.G.Harris
et al.
(2015).
Structural Studies of Geosmin Synthase, a Bifunctional Sesquiterpene Synthase with αα Domain Architecture That Catalyzes a Unique Cyclization-Fragmentation Reaction Sequence.
Biochemistry,
54,
7142-7155.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-Sep-15
|
Release date:
|
09-Dec-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9X839
(CYC2_STRCO) -
Germacradienol/geosmin synthase from Streptomyces coelicolor (strain ATCC BAA-471 / A3(2) / M145)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
726 a.a.
322 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.99.16
- geosmin synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(1E,4S,5E,7R)-germacra-110,5-dien-11-ol + H2O = --geosmin + acetone
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
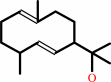 (1E,4S,5E,7R)-germacra-1(10),5-dien-11-ol
(1E,4S,5E,7R)-germacra-1(10),5-dien-11-ol
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
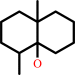 (-)-geosmin
(-)-geosmin
|
+
|
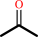 acetone
acetone
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.3.22
- germacradienol synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate + H2O = (1E,4S,5E,7R)-germacra-110,5-dien- 11-ol + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
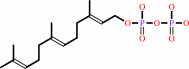 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
(1E,4S,5E,7R)-germacra-1(10),5-dien- 11-ol
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.3.75
- (-)-germacrene D synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate = --germacrene D + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
=
|
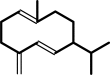 (-)-germacrene D
(-)-germacrene D
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
54:7142-7155
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural Studies of Geosmin Synthase, a Bifunctional Sesquiterpene Synthase with αα Domain Architecture That Catalyzes a Unique Cyclization-Fragmentation Reaction Sequence.
|
|
G.G.Harris,
P.M.Lombardi,
T.A.Pemberton,
T.Matsui,
T.M.Weiss,
K.E.Cole,
M.Köksal,
F.V.Murphy,
L.S.Vedula,
W.K.Chou,
D.E.Cane,
D.W.Christianson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Geosmin synthase from Streptomyces coelicolor (ScGS) catalyzes an unusual,
metal-dependent terpenoid cyclization and fragmentation reaction sequence. Two
distinct active sites are required for catalysis: the N-terminal domain
catalyzes the ionization and cyclization of farnesyl diphosphate to form
germacradienol and inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi), and the C-terminal domain
catalyzes the protonation, cyclization, and fragmentation of germacradienol to
form geosmin and acetone through a retro-Prins reaction. A unique αα domain
architecture is predicted for ScGS based on amino acid sequence: each domain
contains the metal-binding motifs typical of a class I terpenoid cyclase, and
each domain requires Mg(2+) for catalysis. Here, we report the X-ray crystal
structure of the unliganded N-terminal domain of ScGS and the structure of its
complex with three Mg(2+) ions and alendronate. These structures highlight
conformational changes required for active site closure and catalysis. Although
neither full-length ScGS nor constructs of the C-terminal domain could be
crystallized, homology models of the C-terminal domain were constructed on the
basis of ∼36% sequence identity with the N-terminal domain. Small-angle X-ray
scattering experiments yield low-resolution molecular envelopes into which the
N-terminal domain crystal structure and the C-terminal domain homology model
were fit, suggesting possible αα domain architectures as frameworks for
bifunctional catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

