 |
PDBsum entry 5cql
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Gtb mutant with mercury - e303a
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Histo-blood group abo system transferase. Chain: x. Fragment: catalytic domain (unp residues 64-354). Synonym: fucosylglycoprotein 3-alpha-galactosyltransferase, fucosylglycoprotein alpha-n-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, glycoprotein-fucosylgalactoside alpha-n- acetylgalactosaminyltransferase,glycoprotein-fucosylgalactoside alpha-galactosyltransferase,histo-blood group a transferase,a transferase,histo-blood group b transferase,b transferase,nagat.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: abo. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.69Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.176
|
R-free:
|
0.207
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.M.L.Gagnon,R.J.Blackler
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
R.J.Blackler
et al.
(2017).
Glycosyltransfer in mutants of putative catalytic residue Glu303 of the human ABO(H) A and B blood group glycosyltransferases GTA and GTB proceeds through a labile active site.
Glycobiology,
27,
370-380.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Jul-15
|
Release date:
|
26-Oct-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P16442
(BGAT_HUMAN) -
Histo-blood group ABO system transferase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
354 a.a.
261 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 4 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.1.37
- fucosylgalactoside 3-alpha-galactosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-galactosyl derivative + UDP-alpha-D- galactose = an alpha-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-[alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)]-beta-D- galactosyl derivative + UDP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-galactosyl derivative
|
+
|
UDP-alpha-D- galactose
|
=
|
alpha-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-[alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)]-beta-D- galactosyl derivative
|
+
|
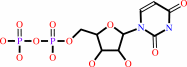 UDP
UDP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.1.40
- glycoprotein-fucosylgalactoside alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-galactosyl derivative + UDP-N-acetyl- alpha-D-galactosamine = an N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosaminyl-(1->3)-[alpha- L-fucosyl-(1->2)]-beta-D-galactosyl derivative + UDP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-galactosyl derivative
|
+
|
UDP-N-acetyl- alpha-D-galactosamine
|
=
|
N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosaminyl-(1->3)-[alpha- L-fucosyl-(1->2)]-beta-D-galactosyl derivative
|
+
|
 UDP
UDP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Glycobiology
27:370-380
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Glycosyltransfer in mutants of putative catalytic residue Glu303 of the human ABO(H) A and B blood group glycosyltransferases GTA and GTB proceeds through a labile active site.
|
|
R.J.Blackler,
S.M.Gagnon,
R.Polakowski,
N.L.Rose,
R.B.Zheng,
J.A.Letts,
A.R.Johal,
B.Schuman,
S.N.Borisova,
M.M.Palcic,
S.V.Evans.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The homologous glycosyltransferases α-1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
(GTA) and α-1,3-galactosyltransferase (GTB) carry out the final synthetic step
of the closely related human ABO(H) blood group A and B antigens. The catalytic
mechanism of these model retaining enzymes remains under debate, where Glu303
has been suggested to act as a putative nucleophile in a double displacement
mechanism, a local dipole stabilizing the intermediate in an orthogonal
associative mechanism or a general base to stabilize the reactive oxocarbenium
ion-like intermediate in an SNi-like mechanism. Kinetic analysis of GTA and GTB
point mutants E303C, E303D, E303Q and E303A shows that despite the enzymes
having nearly identical sequences, the corresponding mutants of GTA/GTB have up
to a 13-fold difference in their residual activities relative to wild type.
High-resolution single crystal X-ray diffraction studies reveal, surprisingly,
that the mutated Cys, Asp and Gln functional groups are no more than 0.8 Å
further from the anomeric carbon of donor substrate compared to wild type.
However, complicating the analysis is the observation that Glu303 itself plays a
critical role in maintaining the stability of a strained "double-turn"
in the active site through several hydrogen bonds, and any mutation other than
E303Q leads to significantly higher thermal motion or even disorder in the
substrate recognition pockets. Thus, there is a remarkable juxtaposition of the
mutants E303C and E303D, which retain significant activity despite disrupted
active site architecture, with GTB/E303Q, which maintains active site
architecture but exhibits zero activity. These findings indicate that
nucleophilicity at position 303 is more catalytically valuable than active site
stability and highlight the mechanistic elasticity of these enzymes.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

