 |
PDBsum entry 5ci3

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5ci3
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Ribonucleotide reductase y122 2,3,5-f3y variant
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase 1 subunit beta. Chain: a. Synonym: protein b2,protein r2,ribonucleotide reductase 1. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli o157:h7. Organism_taxid: 83334. Gene: nrdb, ftsb, z3491, ecs3118. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.168
|
R-free:
|
0.212
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.A.Funk,C.L.Drennan
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
P.H.Oyala
et al.
(2016).
Biophysical Characterization of Fluorotyrosine Probes Site-Specifically Incorporated into Enzymes: E. coli Ribonucleotide Reductase As an Example.
J Am Chem Soc,
138,
7951-7964.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
10-Jul-15
|
Release date:
|
13-Jul-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P69925
(RIR2_ECO57) -
Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase 1 subunit beta from Escherichia coli O157:H7
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
376 a.a.
349 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.17.4.1
- ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-diphosphate + [thioredoxin]-disulfide + H2O = a ribonucleoside 5'-diphosphate + [thioredoxin]-dithiol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate
2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate
|
+
|
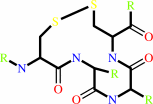 thioredoxin disulfide
thioredoxin disulfide
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
=
|
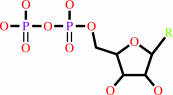 ribonucleoside diphosphate
ribonucleoside diphosphate
|
+
|
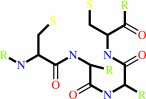 thioredoxin
thioredoxin
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(3+) or adenosylcob(III)alamin or Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Fe(3+)
|
or
|
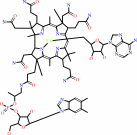 adenosylcob(III)alamin
adenosylcob(III)alamin
|
or
|
Mn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
138:7951-7964
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Biophysical Characterization of Fluorotyrosine Probes Site-Specifically Incorporated into Enzymes: E. coli Ribonucleotide Reductase As an Example.
|
|
P.H.Oyala,
K.R.Ravichandran,
M.A.Funk,
P.A.Stucky,
T.A.Stich,
C.L.Drennan,
R.D.Britt,
J.Stubbe.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Fluorinated tyrosines (FnY's, n = 2 and 3) have been site-specifically
incorporated into E. coli class Ia ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) using the
recently evolved M. jannaschii Y-tRNA synthetase/tRNA pair. Class Ia RNRs
require four redox active Y's, a stable Y radical (Y·) in the β subunit
(position 122 in E. coli), and three transiently oxidized Y's (356 in β and 731
and 730 in α) to initiate the radical-dependent nucleotide reduction process.
FnY (3,5; 2,3; 2,3,5; and 2,3,6) incorporation in place of Y122-β and the X-ray
structures of each resulting β with a diferric cluster are reported and
compared with wt-β2 crystallized under the same conditions. The essential
diferric-FnY· cofactor is self-assembled from apo FnY-β2, Fe(2+), and O2 to
produce ∼1 Y·/β2 and ∼3 Fe(3+)/β2. The FnY· are stable and active in
nucleotide reduction with activities that vary from 5% to 85% that of wt-β2.
Each FnY·-β2 has been characterized by 9 and 130 GHz electron paramagnetic
resonance and high-field electron nuclear double resonance spectroscopies. The
hyperfine interactions associated with the (19)F nucleus provide unique
signatures of each FnY· that are readily distinguishable from unlabeled Y·'s.
The variability of the abiotic FnY pKa's (6.4 to 7.8) and reduction potentials
(-30 to +130 mV relative to Y at pH 7.5) provide probes of enzymatic reactions
proposed to involve Y·'s in catalysis and to investigate the importance and
identity of hopping Y·'s within redox active proteins proposed to protect them
from uncoupled radical chemistry.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

