 |
PDBsum entry 4zzh

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase/hydrolase activator
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4zzh
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.286
- protein acetyllysine N-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-acetyl-L-lysyl-[protein] + NAD+ + H2O = 2''-O-acetyl-ADP-D-ribose + nicotinamide + L-lysyl-[protein]
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-acetyl-L-lysyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
2''-O-acetyl-ADP-D-ribose
|
+
|
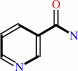 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
L-lysyl-[protein]
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Commun
6:7645
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystallographic structure of a small molecule SIRT1 activator-enzyme complex.
|
|
H.Dai,
A.W.Case,
T.V.Riera,
T.Considine,
J.E.Lee,
Y.Hamuro,
H.Zhao,
Y.Jiang,
S.M.Sweitzer,
B.Pietrak,
B.Schwartz,
C.A.Blum,
J.S.Disch,
R.Caldwell,
B.Szczepankiewicz,
C.Oalmann,
P.Yee Ng,
B.H.White,
R.Casaubon,
R.Narayan,
K.Koppetsch,
F.Bourbonais,
B.Wu,
J.Wang,
D.Qian,
F.Jiang,
C.Mao,
M.Wang,
E.Hu,
J.C.Wu,
R.B.Perni,
G.P.Vlasuk,
J.L.Ellis.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
SIRT1, the founding member of the mammalian family of seven NAD(+)-dependent
sirtuins, is composed of 747 amino acids forming a catalytic domain and extended
N- and C-terminal regions. We report the design and characterization of an
engineered human SIRT1 construct (mini-hSIRT1) containing the minimal structural
elements required for lysine deacetylation and catalytic activation by small
molecule sirtuin-activating compounds (STACs). Using this construct, we solved
the crystal structure of a mini-hSIRT1-STAC complex, which revealed the
STAC-binding site within the N-terminal domain of hSIRT1. Together with
hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS) and site-directed
mutagenesis using full-length hSIRT1, these data establish a specific
STAC-binding site and identify key intermolecular interactions with hSIRT1. The
determination of the interface governing the binding of STACs with human SIRT1
facilitates greater understanding of STAC activation of this enzyme, which holds
significant promise as a therapeutic target for multiple human diseases.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

