 |
PDBsum entry 4zwu
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of organophosphate anhydrolase/prolidase mutant y212f, v342l, i215y
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Organophosphate anhydrolase/prolidase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: x-pro dipeptidase,dfpase,imidodipeptidase,organophosphorus acid anhydrolase 2,opaa-2,paraoxon hydrolase,phosphotriesterase, proline dipeptidase,prolidase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Alteromonas sp.. Organism_taxid: 232. Gene: pepq, opaa. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.172
|
R-free:
|
0.219
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.M.Daczkowski,S.D.Pegan,S.P.Harvey
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.M.Daczkowski
et al.
(2015).
Engineering the Organophosphorus Acid Anhydrolase Enzyme for Increased Catalytic Efficiency and Broadened Stereospecificity on Russian VX.
Biochemistry,
54,
6423-6433.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-May-15
|
Release date:
|
14-Oct-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q44238
(PEPQ_ALTSX) -
Xaa-Pro dipeptidase from Alteromonas sp
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
517 a.a.
435 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 9 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.8.1
- aryldialkylphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
An aryl dialkyl phosphate + H2O = dialkyl phosphate + an aryl alcohol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
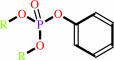 aryl dialkyl phosphate
aryl dialkyl phosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
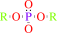 dialkyl phosphate
dialkyl phosphate
|
+
|
aryl alcohol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Divalent cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.4.13.9
- Xaa-Pro dipeptidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
Xaa-L-Pro dipeptide + H2O = an L-alpha-amino acid + L-proline
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Xaa-L-Pro dipeptide
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
L-alpha-amino acid
|
+
|
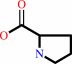 L-proline
L-proline
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.8.2.2
- diisopropyl-fluorophosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
diisopropyl fluorophosphate + H2O = diisopropyl phosphate + fluoride + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 diisopropyl fluorophosphate
diisopropyl fluorophosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
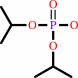 diisopropyl phosphate
diisopropyl phosphate
|
+
|
fluoride
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 44.44% similarity
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
54:6423-6433
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Engineering the Organophosphorus Acid Anhydrolase Enzyme for Increased Catalytic Efficiency and Broadened Stereospecificity on Russian VX.
|
|
C.M.Daczkowski,
S.D.Pegan,
S.P.Harvey.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The enzyme organophosphorus acid anhydrolase (OPAA), from Alteromonas sp. JD6.5,
has been shown to rapidly catalyze the hydrolysis of a number of toxic
organophosphorus compounds, including several G-type chemical nerve agents. The
enzyme was cloned into Escherichia coli and can be produced up to approximately
50% of cellular protein. There have been no previous reports of OPAA activity on
VR {Russian VX, O-isobutyl S-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl] methylphosphonothioate},
and our studies reported here show that wild-type OPAA has poor catalytic
efficacy toward VR. However, via application of a structurally aided protein
engineering approach, significant improvements in catalytic efficiency were
realized via optimization of the small pocket within the OPAA's
substrate-binding site. This optimization involved alterations at only three
amino acid sites resulting in a 30-fold increase in catalytic efficiency toward
racemic VR, with a strong stereospecificity toward the P(+) enantiomer. X-ray
structures of this mutant as well as one of its predecessors provide potential
structural rationales for their effect on the OPAA active site. Additionally, a
fourth mutation at a site near the small pocket was found to relax the
stereospecificity of the OPAA enzyme. Thus, it allows the altered enzyme to
effectively process both VR enantiomers and should be a useful genetic
background in which to seek further improvements in OPAA VR activity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

