 |
PDBsum entry 4zwi

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase/lyase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4zwi
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
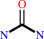 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
24:1800-1807
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Observed surface lysine acetylation of human carbonic anhydrase II expressed in Escherichia coli.
|
|
B.P.Mahon,
C.L.Lomelino,
A.L.Salguero,
J.M.Driscoll,
M.A.Pinard,
R.McKenna.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Acetylation of surface lysine residues of proteins has been observed in
Escherichia coli (E. coli), an organism that has been extensively utilized for
recombinant protein expression. This post-translational modification is shown to
be important in various processes such as metabolism, stress-response,
transcription, and translation. As such, utilization of E. coli expression
systems for protein production may yield non-native acetylation events of
surface lysine residues. Here we present the crystal structures of wild-type and
a variant of human carbonic anhydrase II (hCA II) that have been expressed in E.
coli and exhibit surface lysine acetylation and we speculate on the effect this
has on the conformational stability of each enzyme. Both structures were
determined to 1.6 Å resolution and show clear electron density for lysine
acetylation. The lysine acetylation does not distort the structure and the
surface lysine acetylation events most likely do not interfere with the
biological interpretation. However, there is a reduction in conformational
stability in the hCA II variant compared to wild type (∼4°C decrease). This
may be due to other lysine acetylation events that have occurred but are not
visible in the crystal structure due to intrinsic disorder. Therefore, surface
lysine acetylation events may affect overall protein stability and
crystallization, and should be considered when using E. coli expression systems.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

