 |
PDBsum entry 4zvv

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4zvv
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Lactate dehydrogenase a in complex with a trisubstituted piperidine-2, 4-dione inhibitor gne-140
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
L-lactate dehydrogenase a chain. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: ldh-a,cell proliferation-inducing gene 19 protein,ldh muscle subunit,ldh-m,renal carcinoma antigen ny-ren-59. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: ldha, pig19. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.233
|
R-free:
|
0.259
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.Li,Z.Chen,C.Eigenbrot
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.Boudreau
et al.
(2016).
Metabolic plasticity underpins innate and acquired resistance to LDHA inhibition.
Nat Chem Biol,
12,
779-786.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
18-May-15
|
Release date:
|
18-May-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00338
(LDHA_HUMAN) -
L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
332 a.a.
331 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.27
- L-lactate dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(S)-lactate + NAD+ = pyruvate + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
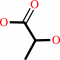 (S)-lactate
(S)-lactate
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Chem Biol
12:779-786
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Metabolic plasticity underpins innate and acquired resistance to LDHA inhibition.
|
|
A.Boudreau,
H.E.Purkey,
A.Hitz,
K.Robarge,
D.Peterson,
S.Labadie,
M.Kwong,
R.Hong,
M.Gao,
C.Del Nagro,
R.Pusapati,
S.Ma,
L.Salphati,
J.Pang,
A.Zhou,
T.Lai,
Y.Li,
Z.Chen,
B.Wei,
I.Yen,
S.Sideris,
M.McCleland,
R.Firestein,
L.Corson,
A.Vanderbilt,
S.Williams,
A.Daemen,
M.Belvin,
C.Eigenbrot,
P.K.Jackson,
S.Malek,
G.Hatzivassiliou,
D.Sampath,
M.Evangelista,
T.O'Brien.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Metabolic reprogramming in tumors represents a potential therapeutic target.
Herein we used shRNA depletion and a novel lactate dehydrogenase (LDHA)
inhibitor, GNE-140, to probe the role of LDHA in tumor growth in vitro and in
vivo. In MIA PaCa-2 human pancreatic cells, LDHA inhibition rapidly affected
global metabolism, although cell death only occurred after 2 d of continuous
LDHA inhibition. Pancreatic cell lines that utilize oxidative phosphorylation
(OXPHOS) rather than glycolysis were inherently resistant to GNE-140, but could
be resensitized to GNE-140 with the OXPHOS inhibitor phenformin. Acquired
resistance to GNE-140 was driven by activation of the AMPK-mTOR-S6K signaling
pathway, which led to increased OXPHOS, and inhibitors targeting this pathway
could prevent resistance. Thus, combining an LDHA inhibitor with compounds
targeting the mitochondrial or AMPK-S6K signaling axis may not only broaden the
clinical utility of LDHA inhibitors beyond glycolytically dependent tumors but
also reduce the emergence of resistance to LDHA inhibition.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

