 |
PDBsum entry 4zup

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase/hydrolase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4zup
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.48
- acetylspermidine deacetylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N8-acetylspermidine + H2O = spermidine + acetate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 N(8)-acetylspermidine
N(8)-acetylspermidine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
spermidine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 42.86% similarity
|
+
|
acetate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.62
- acetylputrescine deacetylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-acetylputrescine + H2O = putrescine + acetate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 N-acetylputrescine
N-acetylputrescine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
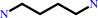 putrescine
putrescine
|
+
|
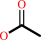 acetate
acetate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
54:4692-4703
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Polyamine Deacetylase Inhibitors, and High-Resolution Crystal Structures of Their Complexes with Acetylpolyamine Amidohydrolase.
|
|
C.Decroos,
D.W.Christianson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Polyamines are essential aliphatic polycations that bind to nucleic acids and
accordingly are involved in a variety of cellular processes. Polyamine function
can be regulated by acetylation and deacetylation, just as histone function can
be regulated by lysine acetylation and deacetylation. Acetylpolyamine
amidohydrolase (APAH) from Mycoplana ramosa is a zinc-dependent polyamine
deacetylase that shares approximately 20% amino acid sequence identity with
human histone deacetylases. We now report the X-ray crystal structures of
APAH-inhibitor complexes in a new and superior crystal form that diffracts to
very high resolution (1.1-1.4 Å). Inhibitors include previously synthesized
analogues of N(8)-acetylspermidine bearing trifluoromethylketone, thiol, and
hydroxamate zinc-binding groups [Decroos, C., Bowman, C. M., and Christianson,
D. W. (2013) Bioorg. Med. Chem. 21, 4530], and newly synthesized hydroxamate
analogues of shorter, monoacetylated diamines, the most potent of which is the
hydroxamate analogue of N-acetylcadaverine (IC50 = 68 nM). The high-resolution
crystal structures of APAH-inhibitor complexes provide key inferences about the
inhibition and catalytic mechanism of zinc-dependent deacetylases. For example,
the trifluoromethylketone analogue of N(8)-acetylspermidine binds as a
tetrahedral gem-diol that mimics the tetrahedral intermediate and its flanking
transition states in catalysis. Surprisingly, this compound is also a potent
inhibitor of human histone deacetylase 8 with an IC50 of 260 nM. Crystal
structures of APAH-inhibitor complexes are determined at the highest resolution
of any currently existing zinc deacetylase structure and thus represent the most
accurate reference points for understanding structure-mechanism and
structure-inhibition relationships in this critically important enzyme family.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

