 |
PDBsum entry 4zk6
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.72
- quinolinate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
iminosuccinate + dihydroxyacetone phosphate = quinolinate + phosphate + 2 H2O + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 iminosuccinate
iminosuccinate
|
+
|
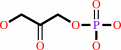 dihydroxyacetone phosphate
dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
=
|
 quinolinate
quinolinate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Iron-sulfur
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Iron-sulfur
Iron-sulfur
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
138:7224-7227
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of Quinolinate Synthase from Pyrococcus horikoshii in the Presence of Its Product, Quinolinic Acid.
|
|
O.A.Esakova,
A.Silakov,
T.L.Grove,
A.H.Saunders,
M.I.McLaughlin,
N.H.Yennawar,
S.J.Booker.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Quinolinic acid (QA) is a common intermediate in the biosynthesis of
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(+)) and its derivatives in all organisms
that synthesize the molecule de novo. In most prokaryotes, it is formed from the
condensation of dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and aspartate-enamine by the
action of quinolinate synthase (NadA). NadA contains a [4Fe-4S] cluster cofactor
with a unique, non-cysteinyl-ligated, iron ion (Fea), which is proposed to bind
the hydroxyl group of a postulated intermediate in the last step of the reaction
to facilitate a dehydration. However, direct evidence for this role in catalysis
has yet to be provided. Herein, we present the structure of NadA in the presence
of the product of its reaction, QA. We find that N1 and the C7 carboxylate group
of QA ligate to Fea in a bidentate fashion, which is confirmed by Hyperfine
Sublevel Correlation (HYSCORE) spectroscopy. This binding mode would place the
C5 hydroxyl group of the postulated final intermediate distal to Fea and
virtually incapable of coordinating to it. The structure shows that three
strictly conserved amino acids, Glu198, Tyr109, and Tyr23, are in close
proximity to the bound product. Substitution of these amino acids with Gln, Phe,
and Phe, respectively, leads to complete loss of activity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

