 |
PDBsum entry 4zdl
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The crystal structure of the t325s mutant of the human holo sepsecs
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
O-phosphoseryl-tRNA(sec) selenium transferase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: liver-pancreas antigen,lp,sla-p35,sla/lp autoantigen, selenocysteine synthase,sec synthase,selenocysteinyl-tRNA(sec) synthase,sep-trna:sec-tRNA synthase,sepsecs,soluble liver antigen, sla,uga suppressor tRNA-associated protein,tRNA(ser/sec)-associated antigenic protein. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: sepsecs, trnp48. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.26Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.166
|
R-free:
|
0.221
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.L.French,M.Simonovic
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.K.Puppala
et al.
(2016).
Structural basis for early-onset neurological disorders caused by mutations in human selenocysteine synthase.
Sci Rep,
6,
32563.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
17-Apr-15
|
Release date:
|
20-Apr-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9HD40
(SPCS_HUMAN) -
O-phosphoseryl-tRNA(Sec) selenium transferase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
501 a.a.
444 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.9.1.2
- O-phospho-L-seryl-tRNA(Sec):L-selenocysteinyl-tRNA synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
O-phospho-L-seryl-tRNA(Sec) + selenophosphate + H2O = L-selenocysteinyl- tRNA(Sec) + 2 phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
O-phospho-L-seryl-tRNA(Sec)
|
+
|
 selenophosphate
selenophosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
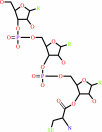 L-selenocysteinyl- tRNA(Sec)
L-selenocysteinyl- tRNA(Sec)
|
+
|
 2
×
phosphate
2
×
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLR)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Sci Rep
6:32563
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for early-onset neurological disorders caused by mutations in human selenocysteine synthase.
|
|
A.K.Puppala,
R.L.French,
D.Matthies,
U.Baxa,
S.Subramaniam,
M.Simonović.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Selenocysteine synthase (SepSecS) catalyzes the terminal reaction of
selenocysteine, and is vital for human selenoproteome integrity. Autosomal
recessive inheritance of mutations in SepSecS-Ala239Thr, Thr325Ser, Tyr334Cys
and Tyr429*-induced severe, early-onset, neurological disorders in distinct
human populations. Although harboring different mutant alleles, patients
presented remarkably similar phenotypes typified by cerebellar and cerebral
atrophy, seizures, irritability, ataxia, and extreme spasticity. However, it has
remained unclear how these genetic alterations affected the structure of SepSecS
and subsequently elicited the development of a neurological pathology. Herein,
our biophysical and structural characterization demonstrates that, with the
exception of Tyr429*, pathogenic mutations decrease protein stability and
trigger protein misfolding. We propose that the reduced stability and increased
propensity towards misfolding are the main causes for the loss of SepSecS
activity in afflicted patients, and that these factors contribute to disease
progression. We also suggest that misfolding of enzymes regulating protein
synthesis should be considered in the diagnosis and study of childhood
neurological disorders.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

