 |
PDBsum entry 4zcs
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of thE C-terminal catalytic domain of plasmodium falciparum ctp:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase in complex with cdp-choline
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase. Chain: a, c, e, b, d, f. Fragment: unp residues 581-775. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Plasmodium falciparum (isolate 3d7). Organism_taxid: 36329. Gene: pf3d7_1316600. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.45Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.183
|
R-free:
|
0.234
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
E.Guca,F.Hoh,J.-F.Guichou,R.Cerdan
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
E.Guca
et al.
(2018).
Structural determinants of the catalytic mechanism of Plasmodium CCT, a key enzyme of malaria lipid biosynthesis.
Sci Rep,
8,
11215.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
16-Apr-15
|
Release date:
|
17-Aug-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q8IEE9
(Q8IEE9_PLAF7) -
choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase from Plasmodium falciparum (isolate 3D7)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
896 a.a.
141 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.7.15
- choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
phosphocholine + CTP + H+ = CDP-choline + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
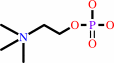 phosphocholine
phosphocholine
|
+
|
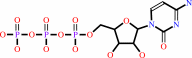 CTP
CTP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
CDP-choline
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Sci Rep
8:11215
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural determinants of the catalytic mechanism of Plasmodium CCT, a key enzyme of malaria lipid biosynthesis.
|
|
E.Guca,
G.N.Nagy,
F.Hajdú,
L.Marton,
R.Izrael,
F.Hoh,
Y.Yang,
H.Vial,
B.G.Vértessy,
J.F.Guichou,
R.Cerdan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The development of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, in the human
erythrocyte, relies on phospholipid metabolism to fulfil the massive need for
membrane biogenesis. Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is the most abundant phospholipid
in Plasmodium membranes. PC biosynthesis is mainly ensured by the de novo
Kennedy pathway that is considered as an antimalarial drug target. The
CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase (CCT) catalyses the rate-limiting step
of the Kennedy pathway. Here we report a series of structural snapshots of the
PfCCT catalytic domain in its free, substrate- and product-complexed states that
demonstrate the conformational changes during the catalytic mechanism.
Structural data show the ligand-dependent conformational variations of a
flexible lysine. Combined kinetic and ligand-binding analyses confirm the
catalytic roles of this lysine and of two threonine residues of the helix αE.
Finally, we assessed the variations in active site residues between Plasmodium
and mammalian CCT which could be exploited for future antimalarial drug design.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

