 |
PDBsum entry 4z1y
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.11
- phosphopyruvate hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(2R)-2-phosphoglycerate = phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(2R)-2-phosphoglycerate
|
=
|
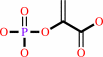 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 90.91% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Front Bioeng Biotechnol
3:74
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Biochemical and Structural Characterization of Enolase from Chloroflexus aurantiacus: Evidence for a Thermophilic Origin.
|
|
O.A.Zadvornyy,
E.S.Boyd,
M.C.Posewitz,
N.A.Zorin,
J.W.Peters.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Enolase catalyzes the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate
during both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, and is required by all three domains
of life. Here, we report the purification and biochemical and structural
characterization of enolase from Chloroflexus aurantiacus, a thermophilic
anoxygenic phototroph affiliated with the green non-sulfur bacteria. The protein
was purified as a homodimer with a subunit molecular weight of 46 kDa. The
temperature optimum for enolase catalysis was 80°C, close to the measured
thermal stability of the protein which was determined to be 75°C, while the pH
optimum for enzyme activity was 6.5. The specific activities of purified enolase
determined at 25 and 80°C were 147 and 300 U mg(-1) of protein,
respectively. K m values for the 2-phosphoglycerate/phosphoenolpyruvate reaction
determined at 25 and 80°C were 0.16 and 0.03 mM, respectively. The K m values
for Mg(2+) binding at these temperatures were 2.5 and 1.9 mM, respectively.
When compared to enolase from mesophiles, the biochemical and structural
properties of enolase from C. aurantiacus are consistent with this being
thermally adapted. These data are consistent with the results of our
phylogenetic analysis of enolase, which reveal that enolase has a thermophilic
origin.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

