 |
PDBsum entry 4y2s

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4y2s
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.76
- lipid-phosphate phosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(9S,10S)-10-hydroxy-9-(phosphooxy)octadecanoate + H2O = (9S,10S)-9,10- dihydroxyoctadecanoate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(9S,10S)-10-hydroxy-9-(phosphooxy)octadecanoate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
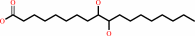 (9S,10S)-9,10- dihydroxyoctadecanoate
(9S,10S)-9,10- dihydroxyoctadecanoate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.3.2.10
- soluble epoxide hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an epoxide + H2O = an ethanediol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
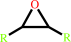 epoxide
epoxide
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
ethanediol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Bioorg Med Chem Lett
23:2310-2317
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Identification of N-ethylmethylamine as a novel scaffold for inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase by crystallographic fragment screening.
|
|
Y.Amano,
E.Tanabe,
T.Yamaguchi.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is a potential target for the treatment of
inflammation and hypertension. X-ray crystallographic fragment screening was
used to identify fragment hits and their binding modes. Eight fragment hits were
identified via soaking of sEH crystals with fragment cocktails, and the
co-crystal structures of these hits were determined via individual soaking.
Based on the binding mode, N-ethylmethylamine was identified as a promising
scaffold that forms hydrogen bonds with the catalytic residues of sEH, Asp335,
Tyr383, and Tyr466. Compounds containing this scaffold were selected from an
in-house chemical library and assayed. Although the starting fragment had a weak
inhibitory activity (IC50: 800μM), we identified potent inhibitors including
2-({[2-(adamantan-1-yl)ethyl]amino}methyl)phenol exhibiting the highest
inhibitory activity (IC50: 0.51μM). This corresponded to a more than 1500-fold
increase in inhibitory activity compared to the starting fragment. Co-crystal
structures of the hit compounds demonstrate that the binding of
N-ethylmethylamine to catalytic residues is similar to that of the starting
fragment. We therefore consider crystallographic fragment screening to be
appropriate for the identification of weak but promising fragment hits.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

