 |
PDBsum entry 4xsh

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Signaling protein/transferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4xsh
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.3.6.5.2
- small monomeric GTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
GTP + H2O = GDP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
GTP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 93.94% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
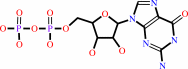 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chain B:
E.C.?
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
290:19423-19432
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Rho GTPase Recognition by C3 Exoenzyme Based on C3-RhoA Complex Structure.
|
|
A.Toda,
T.Tsurumura,
T.Yoshida,
Y.Tsumori,
H.Tsuge.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
C3 exoenzyme is a mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase (ART) that catalyzes transfer of
an ADP-ribose moiety from NAD(+) to Rho GTPases. C3 has long been used to study
the diverse regulatory functions of Rho GTPases. How C3 recognizes its substrate
and how ADP-ribosylation proceeds are still poorly understood. Crystal
structures of C3-RhoA complex reveal that C3 recognizes RhoA via the switch I,
switch II, and interswitch regions. In C3-RhoA(GTP) and C3-RhoA(GDP), switch I
and II adopt the GDP and GTP conformations, respectively, which explains why C3
can ADP-ribosylate both nucleotide forms. Based on structural information, we
successfully changed Cdc42 to an active substrate with combined mutations in the
C3-Rho GTPase interface. Moreover, the structure reflects the close relationship
among Gln-183 in the QXE motif (C3), a modified Asn-41 residue (RhoA) and NC1 of
NAD(H), which suggests that C3 is the prototype ART. These structures show
directly for the first time that the ARTT loop is the key to target protein
recognition, and they also serve to bridge the gaps among independent studies of
Rho GTPases and C3.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

