 |
PDBsum entry 4xii
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
X-ray structure of human butyrylcholinesterase in complex with n-((1- (2,3-dihydro-1h-inden-2-yl)piperidin-3-yl)methyl)-8-hydroxy-n-(2- methoxyethyl)-5-nitroquinoline-7-carboxamide
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Cholinesterase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: acylcholine acylhydrolase,butyrylcholine esterase,choline esterase ii,pseudocholinesterase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: bche, che1. Expressed in: insect cell expression vector ptie1. Expression_system_taxid: 266783
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.208
|
R-free:
|
0.257
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.Knez,B.Boris,N.Coquelle,I.Sosic,R.Sink,X.Brazzolotto,J.Mravljak, J.P.Colletier,S.Gobec
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
D.Knez
et al.
(2015).
Structure-based development of nitroxoline derivatives as potential multifunctional anti-Alzheimer agents.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
23,
4442-4452.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
07-Jan-15
|
Release date:
|
08-Jul-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P06276
(CHLE_HUMAN) -
Cholinesterase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
602 a.a.
528 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.8
- cholinesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an acylcholine + H2O = a carboxylate + choline + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 acylcholine
acylcholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
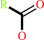 carboxylate
carboxylate
|
+
|
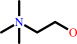 choline
choline
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Bioorg Med Chem Lett
23:4442-4452
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure-based development of nitroxoline derivatives as potential multifunctional anti-Alzheimer agents.
|
|
D.Knez,
B.Brus,
N.Coquelle,
I.Sosič,
R.Šink,
X.Brazzolotto,
J.Mravljak,
J.P.Colletier,
S.Gobec.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Tremendous efforts have been dedicated to the development of effective
therapeutics against Alzheimer's disease, which represents the most common
debilitating neurodegenerative disease. Multifunctional agents are molecules
designed to have simultaneous effects on different pathological processes. Such
compounds represent an emerging strategy for the development of effective
treatments against Alzheimer's disease. Here, we report on the synthesis and
biological evaluation of a series of nitroxoline-based analogs that were
designed by merging the scaffold of 8-hydroxyquinoline with that of a known
selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor that has promising anti-Alzheimer
properties. Most strikingly, compound 8g inhibits self-induced aggregation of
the amyloid beta peptide (Aβ1-42), inhibits with sub-micromolar potency
butyrylcholinesterase (IC50=215nM), and also selectively complexes Cu(2+). Our
study thus designates this compound as a promising multifunctional agent for
therapeutic treatment of Alzheimer's disease. The crystal structure of human
butyrylcholinesterase in complex with compound 8g is also solved, which suggests
ways to further optimize compounds featuring the 8-hydroxyquinoline scaffold.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

