 |
PDBsum entry 4xeh

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4xeh
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.383
- ketol-acid reductoisomerase [NAD(P)(+)].
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
(2R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate + NAD+ = (2S)-2-acetolactate + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
(2R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate + NADP+ = (2S)-2-acetolactate + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
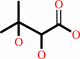 (2R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate
(2R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
(2S)-2-acetolactate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 (2R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate
(2R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
(2S)-2-acetolactate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochem J
468:475-484
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Cofactor specificity motifs and the induced fit mechanism in class I ketol-acid reductoisomerases.
|
|
J.K.Cahn,
S.Brinkmann-Chen,
T.Spatzal,
J.A.Wiig,
A.R.Buller,
O.Einsle,
Y.Hu,
M.W.Ribbe,
F.H.Arnold.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Although most sequenced members of the industrially important ketol-acid
reductoisomerase (KARI) family are class I enzymes, structural studies to date
have focused primarily on the class II KARIs, which arose through domain
duplication. In the present study, we present five new crystal structures of
class I KARIs. These include the first structure of a KARI with a six-residue
β2αB (cofactor specificity determining) loop and an NADPH phosphate-binding
geometry distinct from that of the seven- and 12-residue loops. We also present
the first structures of naturally occurring KARIs that utilize NADH as cofactor.
These results show insertions in the specificity loops that confounded previous
attempts to classify them according to loop length. Lastly, we explore the
conformational changes that occur in class I KARIs upon binding of cofactor and
metal ions. The class I KARI structures indicate that the active sites close
upon binding NAD(P)H, similar to what is observed in the class II KARIs of rice
and spinach and different from the opening of the active site observed in the
class II KARI of Escherichia coli. This conformational change involves a
decrease in the bending of the helix that runs between the domains and a
rearrangement of the nicotinamide-binding site.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

