 |
PDBsum entry 4xds

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase/DNA
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4xds
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase/DNA
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Deoxyguanosinetriphosphate triphosphohydrolase from escherichia coli with nickel
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Deoxyguanosinetriphosphate triphosphohydrolase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Synonym: dgtpase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli (strain k12). Organism_taxid: 83333. Strain: k12. Gene: dgt, b0160, jw0156. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.35Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.174
|
R-free:
|
0.209
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.Singh,D.Gawel,M.Itsko,J.M.Krahn,R.E.London,R.M.Schaaper
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
D.Singh
et al.
(2015).
Structure of Escherichia coli dGTP triphosphohydrolase: a hexameric enzyme with DNA effector molecules.
J Biol Chem,
290,
10418-10429.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Dec-14
|
Release date:
|
25-Feb-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P15723
(DGTP_ECOLI) -
Deoxyguanosinetriphosphate triphosphohydrolase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
505 a.a.
492 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.5.1
- dGTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
dGTP + H2O = 2'-deoxyguanosine + triphosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
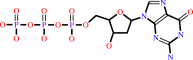 dGTP
dGTP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
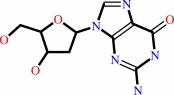 2'-deoxyguanosine
2'-deoxyguanosine
|
+
|
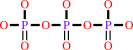 triphosphate
triphosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
290:10418-10429
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of Escherichia coli dGTP triphosphohydrolase: a hexameric enzyme with DNA effector molecules.
|
|
D.Singh,
D.Gawel,
M.Itsko,
A.Hochkoeppler,
J.M.Krahn,
R.E.London,
R.M.Schaaper.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The Escherichia coli dgt gene encodes a dGTP triphosphohydrolase whose detailed
role still remains to be determined. Deletion of dgt creates a mutator
phenotype, indicating that the dGTPase has a fidelity role, possibly by
affecting the cellular dNTP pool. In the present study, we have investigated the
structure of the Dgt protein at 3.1-Å resolution. One of the obtained
structures revealed a protein hexamer that contained two molecules of
single-stranded DNA. The presence of DNA caused significant conformational
changes in the enzyme, including in the catalytic site of the enzyme. Dgt
preparations lacking DNA were able to bind single-stranded DNA with high
affinity (Kd ∼ 50 nm). DNA binding positively affected the activity of the
enzyme: dGTPase activity displayed sigmoidal (cooperative) behavior without DNA
but hyperbolic (Michaelis-Menten) kinetics in its presence, consistent with a
specific lowering of the apparent Km for dGTP. A mutant Dgt enzyme was also
created containing residue changes in the DNA binding cleft. This mutant enzyme,
whereas still active, was incapable of DNA binding and could no longer be
stimulated by addition of DNA. We also created an E. coli strain containing the
mutant dgt gene on the chromosome replacing the wild-type gene. The mutant also
displayed a mutator phenotype. Our results provide insight into the allosteric
regulation of the enzyme and support a physiologically important role of DNA
binding.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

