 |
PDBsum entry 4tk3

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Biosynthetic protein,structural protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4tk3
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.10.1.1
- molybdopterin molybdotransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
adenylyl-molybdopterin + molybdate = Mo-molybdopterin + AMP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
adenylyl-molybdopterin
|
+
|
molybdate
|
=
|
Mo-molybdopterin
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+) or Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.7.75
- molybdopterin adenylyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
molybdopterin + ATP + H+ = adenylyl-molybdopterin + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
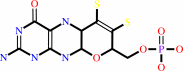 molybdopterin
molybdopterin
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
adenylyl-molybdopterin
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mn(2+) or Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Commun
5:5767
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Molecular basis of the alternative recruitment of GABA(A) versus glycine receptors through gephyrin.
|
|
H.M.Maric,
V.B.Kasaragod,
T.J.Hausrat,
M.Kneussel,
V.Tretter,
K.Strømgaard,
H.Schindelin.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
γ-Aminobutyric acid type A and glycine receptors (GABAARs, GlyRs) are the major
inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors and contribute to many synaptic functions,
dysfunctions and human diseases. GABAARs are important drug targets regulated by
direct interactions with the scaffolding protein gephyrin. Here we deduce the
molecular basis of this interaction by chemical, biophysical and structural
studies of the gephyrin-GABAAR α3 complex, revealing that the N-terminal region
of the α3 peptide occupies the same binding site as the GlyR β subunit,
whereas the C-terminal moiety, which is conserved among all synaptic GABAAR α
subunits, engages in unique interactions. Thermodynamic dissections of the
gephyrin-receptor interactions identify two residues as primary determinants for
gephyrin's subunit preference. This first structural evidence for the
gephyrin-mediated synaptic accumulation of GABAARs offers a framework for future
investigations into the regulation of inhibitory synaptic strength and for the
development of mechanistically and therapeutically relevant compounds targeting
the gephyrin-GABAAR interaction.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

