 |
PDBsum entry 4tk0
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human tankyrase 2 in complex with dpq.
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Tankyrase-2. Chain: a, b, c, d. Fragment: parp, catalytic domain. Synonym: tank2,adp-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 6,artd6, poly [adp-ribose] polymerase 5b,tnks-2,trf1-interacting ankyrin- related adp-ribose polymerase 2,tankyrase ii,tankyrase-like protein, tankyrase-related protein. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: tnks2, parp5b, tank2, tnkl. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.65Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.188
|
R-free:
|
0.225
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
W.Qiu,R.Lam,V.Romanov,R.Gordon,S.Gebremeskel,J.Vodsedalek,C.Thompson, I.Beletskaya,K.P.Battaile,E.F.Pai,N.Y.Chirgadze
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
W.Qiu
et al.
(2014).
Insights into the binding of PARP inhibitors to the catalytic domain of human tankyrase-2.
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
70,
2740-2753.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-May-14
|
Release date:
|
05-Nov-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9H2K2
(TNKS2_HUMAN) -
Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase tankyrase-2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1166 a.a.
199 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.2.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.2.30
- NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
NAD+ + (ADP-D-ribosyl)n-acceptor = nicotinamide + (ADP-D- ribosyl)n+1-acceptor + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
(ADP-D-ribosyl)n-acceptor
|
=
|
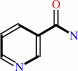 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
(ADP-D- ribosyl)n+1-acceptor
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
70:2740-2753
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Insights into the binding of PARP inhibitors to the catalytic domain of human tankyrase-2.
|
|
W.Qiu,
R.Lam,
O.Voytyuk,
V.Romanov,
R.Gordon,
S.Gebremeskel,
J.Vodsedalek,
C.Thompson,
I.Beletskaya,
K.P.Battaile,
E.F.Pai,
R.Rottapel,
N.Y.Chirgadze.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) family represents a new class of
therapeutic targets with diverse potential disease indications. PARP1 and PARP2
inhibitors have been developed for breast and ovarian tumors manifesting
double-stranded DNA-repair defects, whereas tankyrase 1 and 2 (TNKS1 and TNKS2,
also known as PARP5a and PARP5b, respectively) inhibitors have been developed
for tumors with elevated β-catenin activity. As the clinical relevance of PARP
inhibitors continues to be actively explored, there is heightened interest in
the design of selective inhibitors based on the detailed structural features of
how small-molecule inhibitors bind to each of the PARP family members. Here, the
high-resolution crystal structures of the human TNKS2 PARP domain in complex
with 16 various PARP inhibitors are reported, including the compounds BSI-201,
AZD-2281 and ABT-888, which are currently in Phase 2 or 3 clinical trials. These
structures provide insight into the inhibitor-binding modes for the tankyrase
PARP domain and valuable information to guide the rational design of future
tankyrase-specific inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

