 |
PDBsum entry 4mvh

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase/hydrolase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4mvh
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.4.17
- 3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a nucleoside 3',5'-cyclic phosphate + H2O = a nucleoside 5'-phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
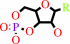 nucleoside 3',5'-cyclic phosphate
nucleoside 3',5'-cyclic phosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
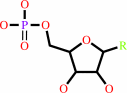 nucleoside 5'-phosphate
nucleoside 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
56:8781-8792
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Design, optimization, and biological evaluation of novel keto-benzimidazoles as potent and selective inhibitors of phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A).
|
|
E.Hu,
R.K.Kunz,
N.Chen,
S.Rumfelt,
A.Siegmund,
K.Andrews,
S.Chmait,
S.Zhao,
C.Davis,
H.Chen,
D.Lester-Zeiner,
J.Ma,
C.Biorn,
J.Shi,
A.Porter,
J.Treanor,
J.R.Allen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Our development of PDE10A inhibitors began with an HTS screening hit (1) that
exhibited both high p-glycoprotein (P-gp) efflux ratios in rat and human and
poor metabolic stability. On the basis of cocrystal structure of 1 in human
PDE10A enzyme, we designed a novel keto-benzimidazole 26 with comparable PDE10A
potency devoid of efflux liabilities. On target in vivo coverage of PDE10A in
rat brain was assessed using our previously reported LC-MS/MS receptor occupancy
(RO) technology. Compound 26 achieved 55% RO of PDE10A at 30 mg/kg po and
covered PDE10A receptors in rat brain in a dose-dependent manner. Cocrystal
structure of 26 in PDE10A confirmed the binding mode of the novel scaffold.
Further optimization resulted in the identification of keto-benzimidazole 34,
which showed an increased in vivo efficacy of 57% RO in rats at 10 mg/kg po and
an improved in vivo rat clearance and oral bioavailability.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

