 |
PDBsum entry 4mql
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of antigen 85c-c209s mutant
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase/mycolyltransferase ag85c. Chain: a. Synonym: dgat, acyl-coa:diacylglycerol acyltransferase, antigen 85 complex c, 85c, ag85c, fibronectin-binding protein c, fbps c. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Organism_taxid: 1773. Gene: fbpc, mpt45, rv0129c, mt0137, mtci5.03c. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.154
|
R-free:
|
0.165
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
L.Favrot,A.E.Grzegorzewicz,D.H.Lajiness,R.K.Marvin,J.Boucau, D.Isailovic,M.Jackson,D.R.Ronning
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
L.Favrot
et al.
(2013).
Mechanism of inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 85 by ebselen.
Nat Commun,
4,
2748.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
16-Sep-13
|
Release date:
|
13-Nov-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P9WQN9
(A85C_MYCTU) -
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase/mycolyltransferase Ag85C from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
340 a.a.
282 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.122
- trehalose O-mycolyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 alpha,alpha'-trehalose 6-mycolate = alpha,alpha'-trehalose 6,6'-bismycolate + alpha,alpha-trehalose
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
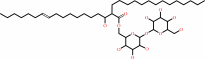 2
×
alpha,alpha'-trehalose 6-mycolate
2
×
alpha,alpha'-trehalose 6-mycolate
|
=
|
 alpha,alpha'-trehalose 6,6'-bismycolate
alpha,alpha'-trehalose 6,6'-bismycolate
|
+
|
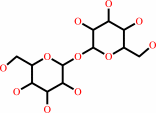 alpha,alpha-trehalose
alpha,alpha-trehalose
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.20
- diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an acyl-CoA + a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol = a triacyl-sn-glycerol + CoA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
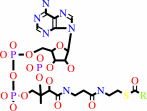 2
×
acyl-CoA
2
×
acyl-CoA
|
+
|
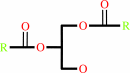 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
|
=
|
triacyl-sn-glycerol
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Commun
4:2748
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanism of inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 85 by ebselen.
|
|
L.Favrot,
A.E.Grzegorzewicz,
D.H.Lajiness,
R.K.Marvin,
J.Boucau,
D.Isailovic,
M.Jackson,
D.R.Ronning.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The increasing prevalence of drug-resistant tuberculosis highlights the need for
identifying new antitubercular drugs that can treat these infections. The
antigen 85 (Ag85) complex has emerged as an intriguing mycobacterial drug target
due to its central role in synthesizing major components of the inner and outer
leaflets of the mycobacterial outer membrane. Here we identify ebselen (EBS) as
a potent inhibitor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Ag85 complex. Mass
spectrometry data show that EBS binds covalently to a cysteine residue (C209)
located near the Ag85C active site. The crystal structure of Ag85C in the
presence of EBS shows that C209 modification restructures the active site,
thereby disrupting the hydrogen-bonded network within the active site that is
essential for enzymatic activity. C209 mutations display marked decreases in
enzymatic activity. These data suggest that compounds using this mechanism of
action will strongly inhibit the Ag85 complex and minimize the selection of drug
resistance.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

