 |
PDBsum entry 4mpy

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4mpy
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
1.85 angstrom resolution crystal structure of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (betb) from staphylococcus aureus (idp00699) in complex with NAD+
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Staphylococcus aureus subsp. Aureus. Organism_taxid: 93062. Strain: col. Gene: betb, sacol2628. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.85Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.127
|
R-free:
|
0.167
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.S.Halavaty,G.Minasov,L.Shuvalova,J.Winsor,S.N.Peterson, W.F.Anderson,Center For Structural Genomics Of Infectious Diseases (Csgid)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.Chen
et al.
(2014).
Structure-based mutational studies of substrate inhibition of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase BetB from Staphylococcus aureus.
Appl Environ Microbiol,
80,
3992-4002.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
14-Sep-13
|
Release date:
|
09-Oct-13
|
|
|
Supersedes:
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
A0A0H2X0S3
(A0A0H2X0S3_STAAC) -
Betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase from Staphylococcus aureus (strain COL)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
496 a.a.
500 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.8
- betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
betaine aldehyde + NAD+ + H2O = glycine betaine + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
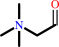 betaine aldehyde
betaine aldehyde
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
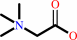 glycine betaine
glycine betaine
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Appl Environ Microbiol
80:3992-4002
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure-based mutational studies of substrate inhibition of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase BetB from Staphylococcus aureus.
|
|
C.Chen,
J.C.Joo,
G.Brown,
E.Stolnikova,
A.S.Halavaty,
A.Savchenko,
W.F.Anderson,
A.F.Yakunin.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Inhibition of enzyme activity by high concentrations of substrate and/or
cofactor is a general phenomenon demonstrated in many enzymes, including
aldehyde dehydrogenases. Here we show that the uncharacterized protein BetB
(SA2613) from Staphylococcus aureus is a highly specific betaine aldehyde
dehydrogenase, which exhibits substrate inhibition at concentrations of betaine
aldehyde as low as 0.15 mM. In contrast, the aldehyde dehydrogenase YdcW from
Escherichia coli, which is also active against betaine aldehyde, shows no
inhibition by this substrate. Using the crystal structures of BetB and YdcW, we
performed a structure-based mutational analysis of BetB and introduced the YdcW
residues into the BetB active site. From a total of 32 mutations, those in five
residues located in the substrate binding pocket (Val288, Ser290, His448,
Tyr450, and Trp456) greatly reduced the substrate inhibition of BetB, whereas
the double mutant protein H448F/Y450L demonstrated a complete loss of substrate
inhibition. Substrate inhibition was also reduced by mutations of the
semiconserved Gly234 (to Ser, Thr, or Ala) located in the BetB NAD(+) binding
site, suggesting some cooperativity between the cofactor and substrate binding
sites. Substrate docking analysis of the BetB and YdcW active sites revealed
that the wild-type BetB can bind betaine aldehyde in both productive and
nonproductive conformations, whereas only the productive binding mode can be
modeled in the active sites of YdcW and the BetB mutant proteins with reduced
substrate inhibition. Thus, our results suggest that the molecular mechanism of
substrate inhibition of BetB is associated with the nonproductive binding of
betaine aldehyde.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

