 |
PDBsum entry 4lw2
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.8.1.7
- cysteine desulfurase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(sulfur carrier)-H + L-cysteine = (sulfur carrier)-SH + L-alanine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(sulfur carrier)-H
|
+
|
 L-cysteine
L-cysteine
|
=
|
(sulfur carrier)-SH
|
+
|
L-alanine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.4.1.16
- selenocysteine lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-selenocysteine + AH2 = hydrogenselenide + L-alanine + A + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
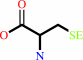 L-selenocysteine
L-selenocysteine
|
+
|
AH2
|
=
|
hydrogenselenide
|
+
|
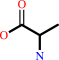 L-alanine
L-alanine
|
+
|
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
288:27172-27180
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural changes during cysteine desulfurase CsdA and sulfur acceptor CsdE interactions provide insight into the trans-persulfuration.
|
|
S.Kim,
S.Park.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In Escherichia coli, three cysteine desulfurases (IscS, SufS, and CsdA) initiate
the delivery of sulfur for various biological processes such as the biogenesis
of Fe-S clusters. The sulfur generated as persulfide on a cysteine residue of
cysteine desulfurases is further transferred to Fe-S scaffolds (e.g. IscU) or to
intermediate cysteine-containing sulfur acceptors (e.g. TusA, SufE, and CsdE)
prior to its utilization. Here, we report the structures of CsdA and the
CsdA-CsdE complex, which provide insight into the sulfur transfer mediated by
the trans-persulfuration reaction. Analysis of the structures indicates that the
conformational flexibility of the active cysteine loop in CsdE is essential for
accepting the persulfide from the cysteine of CsdA. Additionally, CsdA and CsdE
invoke a different binding mode than those of previously reported cysteine
desulfurase (IscS) and sulfur acceptors (TusA and IscU). Moreover, the
conservation of interaction-mediating residues between CsdA/SufS and CsdE/SufE
further suggests that the SufS-SufE interface likely resembles that of CsdA and
CsdE.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

