 |
PDBsum entry 4lph

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4lph
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human fpps in complex with cl03093
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase. Chain: f. Fragment: unp residues 67-419. Synonym: fpp synthase, fps, (2e,6e)-farnesyl diphosphate synthase, dimethylallyltranstransferase, farnesyl diphosphate synthase, geranyltranstransferase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: fdps, fps, kiaa1293. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.186
|
R-free:
|
0.226
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Park,C.Y.Leung,Y.S.Tsantrizos,A.M.Berghuis
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.W.De Schutter
et al.
(2014).
Multistage screening reveals chameleon ligands of the human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase: implications to drug discovery for neurodegenerative diseases.
J Med Chem,
57,
5764-5776.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
16-Jul-13
|
Release date:
|
25-Jun-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P14324
(FPPS_HUMAN) -
Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
419 a.a.
342 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.1
- dimethylallyltranstransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Terpenoid biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
isopentenyl diphosphate + dimethylallyl diphosphate = (2E)- geranyl diphosphate + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
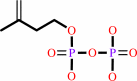 isopentenyl diphosphate
isopentenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
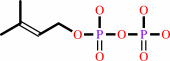 dimethylallyl diphosphate
dimethylallyl diphosphate
|
=
|
(2E)- geranyl diphosphate
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.10
- (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
isopentenyl diphosphate + (2E)-geranyl diphosphate = (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 isopentenyl diphosphate
isopentenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
(2E)-geranyl diphosphate
|
=
|
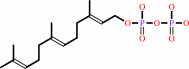 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
57:5764-5776
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Multistage screening reveals chameleon ligands of the human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase: implications to drug discovery for neurodegenerative diseases.
|
|
J.W.De Schutter,
J.Park,
C.Y.Leung,
P.Gormley,
Y.S.Lin,
Z.Hu,
A.M.Berghuis,
J.Poirier,
Y.S.Tsantrizos.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (hFPPS) is the gate-keeper of mammalian
isoprenoids and the key target of bisphosphonate drugs. Bisphosphonates suffer
from poor "drug-like" properties and are mainly effective in treating
skeletal diseases. Recent investigations have implicated hFPPS in various
nonskeletal diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). Analysis of single
nucleotide polymorphisms in the hFPPS gene and mRNA levels in autopsy-confirmed
AD subjects was undertaken, and a genetic link between hFPPS and phosphorylated
tau (P-Tau) levels in the human brain was identified. Elevated P-Tau levels are
strongly implicated in AD progression. The development of nonbisphosphonate
inhibitors can provide molecular tools for validating hFPPS as a therapeutic
target for tauopathy-associated neurodegeneration. A multistage screening
protocol led to the identification of a new monophosphonate chemotype that bind
in an allosteric pocket of hFPPS. Optimization of these compounds could lead to
human therapeutics that block tau metabolism and arrest the progression of
neurodegeneration.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

