 |
PDBsum entry 4lns
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.1.1
- aspartate--ammonia ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-aspartate + NH4+ + ATP = L-asparagine + AMP + diphosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
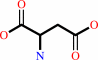 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
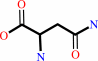 L-asparagine
L-asparagine
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
289:12096-12108
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Identification and functional characterization of a novel bacterial type asparagine synthetase A: a tRNA synthetase paralog from Leishmania donovani.
|
|
R.Manhas,
P.Tripathi,
S.Khan,
B.Sethu Lakshmi,
S.K.Lal,
V.S.Gowri,
A.Sharma,
R.Madhubala.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Asparagine is formed by two structurally distinct asparagine synthetases in
prokaryotes. One is the ammonia-utilizing asparagine synthetase A (AsnA), and
the other is asparagine synthetase B (AsnB) that uses glutamine or ammonia as a
nitrogen source. In a previous investigation using sequence-based analysis, we
had shown that Leishmania spp. possess asparagine-tRNA synthetase paralog
asparagine synthetase A (LdASNA) that is ammonia-dependent. Here, we report the
cloning, expression, and kinetic analysis of ASNA from Leishmania donovani.
Interestingly, LdASNA was both ammonia- and glutamine-dependent. To study the
physiological role of ASNA in Leishmania, gene deletion mutations were attempted
via targeted gene replacement. Gene deletion of LdASNA showed a growth delay in
mutants. However, chromosomal null mutants of LdASNA could not be obtained as
the double transfectant mutants showed aneuploidy. These data suggest that
LdASNA is essential for survival of the Leishmania parasite. LdASNA enzyme was
recalcitrant toward crystallization so we instead crystallized and solved the
atomic structure of its close homolog from Trypanosoma brucei (TbASNA) at 2.2
Å. A very significant conservation in active site residues is observed between
TbASNA and Escherichia coli AsnA. It is evident that the absence of an LdASNA
homolog from humans and its essentiality for the parasites make LdASNA a novel
drug target.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

