 |
PDBsum entry 4l5u
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
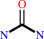 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Arch Biochem Biophys
539:31-37
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural, catalytic and stabilizing consequences of aromatic cluster variants in human carbonic anhydrase II.
|
|
C.D.Boone,
S.Gill,
C.Tu,
D.N.Silverman,
R.McKenna.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The presence of aromatic clusters has been found to be an integral feature of
many proteins isolated from thermophilic microorganisms. Residues found in
aromatic cluster interact via π-π or C-H⋯π bonds between the phenyl rings,
which are among the weakest interactions involved in protein stability. The lone
aromatic cluster in human carbonic anhydrase II (HCA II) is centered on F226
with the surrounding aromatics F66, F95 and W97 located 12 Å posterior the
active site; a location which could facilitate proper protein folding and active
site construction. The role of F226 in the structure, catalytic activity and
thermostability of HCA II was investigated via site-directed mutagenesis of
three variants (F226I/L/W) into this position. The measured catalytic rates of
the F226 variants via (18)O-mass spectrometry were identical to the native
enzyme, but differential scanning calorimetry studies revealed a 3-4 K decrease
in their denaturing temperature. X-ray crystallographic analysis suggests that
the structural basis of this destabilization is via disruption and/or removal of
weak C-H⋯π interactions between F226 to F66, F95 and W97. This study
emphasizes the importance of the delicate arrangement of these weak interactions
among aromatic clusters in overall protein stability.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

