 |
PDBsum entry 4kev
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of ssopox w263l
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aryldialkylphosphatase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: paraoxonase, ssopox, phosphotriesterase-like lactonase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sulfolobus solfataricus. Organism_taxid: 2287. Gene: php, php sso2522, sso2522. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.65Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.205
|
R-free:
|
0.250
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
G.Gotthard,J.Hiblot,E.Chabriere,M.Elias
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Hiblot
et al.
(2013).
Differential active site loop conformations mediate promiscuous activities in the lactonase SsoPox.
Plos One,
8,
e75272.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
26-Apr-13
|
Release date:
|
02-Oct-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q97VT7
(PHP_SULSO) -
Aryldialkylphosphatase from Saccharolobus solfataricus (strain ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
314 a.a.
314 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.8.1
- aryldialkylphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
An aryl dialkyl phosphate + H2O = dialkyl phosphate + an aryl alcohol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
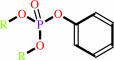 aryl dialkyl phosphate
aryl dialkyl phosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
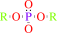 dialkyl phosphate
dialkyl phosphate
|
+
|
aryl alcohol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Divalent cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Plos One
8:e75272
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Differential active site loop conformations mediate promiscuous activities in the lactonase SsoPox.
|
|
J.Hiblot,
G.Gotthard,
M.Elias,
E.Chabriere.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Enzymes are proficient catalysts that enable fast rates of Michaelis-complex
formation, the chemical step and products release. These different steps may
require different conformational states of the active site that have distinct
binding properties. Moreover, the conformational flexibility of the active site
mediates alternative, promiscuous functions. Here we focused on the lactonase
SsoPox from Sulfolobus solfataricus. SsoPox is a native lactonase endowed with
promiscuous phosphotriesterase activity. We identified a position in the active
site loop (W263) that governs its flexibility, and thereby affects the substrate
specificity of the enzyme. We isolated two different sets of substitutions at
position 263 that induce two distinct conformational sampling of the active loop
and characterized the structural and kinetic effects of these substitutions.
These sets of mutations selectively and distinctly mediate the improvement of
the promiscuous phosphotriesterase and oxo-lactonase activities of SsoPox by
increasing active-site loop flexibility. These observations corroborate the idea
that conformational diversity governs enzymatic promiscuity and is a key feature
of protein evolvability.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

