 |
PDBsum entry 4jgq
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The crystal structure of sporulation kinase d mutant sensor domain, r131a, from bacillus subtilis subsp in co-crystallization with pyruvate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Sporulation kinase d. Chain: a, b. Fragment: sensor domain (unp residues 37-250). Synonym: sensor histidine kinase d. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bacillus subtilis subsp. Subtilis. Organism_taxid: 224308. Strain: 168. Gene: bsu13660, kind, ykvd. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 511693.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.63Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.195
|
R-free:
|
0.248
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.Wu,M.Schiffer,M.Gu,A.Joachimiak,Midwest Center For Structural Genomics (Mcsg)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
R.Wu
et al.
(2013).
Insight into the sporulation phosphorelay: crystal structure of the sensor domain of Bacillus subtilis histidine kinase, KinD.
Protein Sci,
22,
564-576.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
01-Mar-13
|
Release date:
|
15-May-13
|
|
|
Supersedes:
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O31671
(KIND_BACSU) -
Sporulation kinase D from Bacillus subtilis (strain 168)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
506 a.a.
203 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.13.3
- histidine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
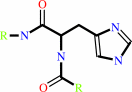 protein L-histidine
protein L-histidine
|
=
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
22:564-576
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Insight into the sporulation phosphorelay: crystal structure of the sensor domain of Bacillus subtilis histidine kinase, KinD.
|
|
R.Wu,
M.Gu,
R.Wilton,
G.Babnigg,
Y.Kim,
P.R.Pokkuluri,
H.Szurmant,
A.Joachimiak,
M.Schiffer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The Bacillus subtilis KinD signal-transducing histidine kinase is a part of the
sporulation phosphorelay known to regulate important developmental decisions
such as sporulation and biofilm formation. We have determined crystal structures
of the extracytoplasmic sensing domain of KinD, which was copurified and
crystallized with a pyruvate ligand. The structure of a ligand-binding site
mutant was also determined; it was copurified and crystallized with an acetate
ligand. The structure of the KinD extracytoplasmic segment is similar to that of
several other sensing domains of signal transduction proteins and is composed of
tandem Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS)-like domains. The KinD ligand-binding site is located
on the membrane distal PAS-like domain and appears to be highly selective; a
single mutation, R131A, abolishes pyruvate binding and the mutant binds acetate
instead. Differential scanning fluorimetry, using a variety of monocarboxylic
and dicarboxylic acids, identified pyruvate, propionate, and butyrate but not
lactate, acetate, or malate as KinD ligands. A recent report found that malate
induces biofilm formation in a KinD-dependent manner. It was suggested that
malate might induce a metabolic shift and increased secretion of the KinD ligand
of unknown identity. The structure and binding assays now suggests that this
ligand is pyruvate and/or other small monocarboxylic acids. In summary, this
study gives a first insight into the identity of a molecular ligand for one of
the five phosphorelay kinases of B. subtilis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

