 |
PDBsum entry 4jfl
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Increasing the efficiency efficiency of ligands for the fk506-binding protein 51 by conformational control: complex of fkbp51 with 6-({(1s, 5r)-3-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenoxy)ethyl]-2-oxo-3,9- diazabicyclo[3.3.1]non-9-yl}sulfonyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2(3h)-one
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase fkbp5. Chain: a. Fragment: unp residues 16-140. Synonym: ppiase fkbp5, 51 kda fk506-binding protein, 51 kda fkbp, fkbp-51, 54 kda progesterone receptor-associated immunophilin, androgen-regulated protein 6, ff1 antigen, fk506-binding protein 5, fkbp-5, fkbp54, p54, hsp90-binding immunophilin, rotamase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: aig6, fkbp5, fkbp51. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.143
|
R-free:
|
0.174
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.Wang,A.Kirschner,A.Fabian,R.Gopalakrishnan,C.Kress,B.Hoogeland, U.Koch,C.Kozany,A.Bracher,F.Hausch
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Y.Wang
et al.
(2013).
Increasing the efficiency of ligands for FK506-binding protein 51 by conformational control.
J Med Chem,
56,
3922-3935.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
28-Feb-13
|
Release date:
|
28-Aug-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q13451
(FKBP5_HUMAN) -
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP5 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
457 a.a.
128 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 4 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
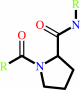 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
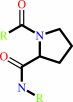 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
56:3922-3935
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Increasing the efficiency of ligands for FK506-binding protein 51 by conformational control.
|
|
Y.Wang,
A.Kirschner,
A.K.Fabian,
R.Gopalakrishnan,
C.Kress,
B.Hoogeland,
U.Koch,
C.Kozany,
A.Bracher,
F.Hausch.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The design of efficient ligands remains a key challenge in drug discovery. In
the quest for lead-like ligands for the FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP51), we
designed two new classes of bicyclic sulfonamides to probe the contribution of
conformational energy in these ligands. The [4.3.1] scaffold had consistently
higher affinity compared to the [3.3.1] or monocyclic scaffolds, which could be
attributed to better preorganization of two key recognition motifs.
Surprisingly, the binding of the rigid [4.3.1] scaffold was enthalpy-driven and
entropically disfavored compared to the flexible analogues. Cocrystal structures
at atomic resolution revealed that the sulfonamide nitrogen in the bicyclic
scaffolds can accept an unusual hydrogen bond from Tyr(113) that mimics the
putative FKBP transition state. This resulted in the first lead-like,
functionally active ligand for FKBP51. Our work exemplifies how atom-efficient
ligands can be achieved by careful conformational control even in very open and
thus difficult binding sites such as FKBP51.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

