 |
PDBsum entry 4jbg

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4jbg
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
1.75a resolution structure of a thermostable alcohol dehydrogenase from pyrobaculum aerophilum
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Alcohol dehydrogenase (zinc). Chain: a, b, c, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Pyrobaculum aerophilum. Organism_taxid: 178306. Strain: atcc 51768 / im2 / dsm 7523 / jcm 9630 / nbrc 100827. Gene: pae2687. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.75Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.153
|
R-free:
|
0.174
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Lovell,K.P.Battaile,A.Vitale,N.Throne,X.Hu,M.Shen,S.D'Auria, D.S.Auld
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.Vitale
et al.
(2013).
Physicochemical characterization of a thermostable alcohol dehydrogenase from Pyrobaculum aerophilum.
Plos One,
8,
e63828.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Feb-13
|
Release date:
|
19-Jun-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q8ZUP0
(Q8ZUP0_PYRAE) -
Alcohol dehydrogenase (Zinc) from Pyrobaculum aerophilum (strain ATCC 51768 / DSM 7523 / JCM 9630 / CIP 104966 / NBRC 100827 / IM2)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
331 a.a.
333 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.1
- alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a primary alcohol + NAD+ = an aldehyde + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
a secondary alcohol + NAD+ = a ketone + NADH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
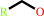 primary alcohol
primary alcohol
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
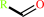 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
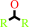 secondary alcohol
secondary alcohol
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
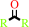 ketone
ketone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+) or Fe cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Plos One
8:e63828
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Physicochemical characterization of a thermostable alcohol dehydrogenase from Pyrobaculum aerophilum.
|
|
A.Vitale,
N.Thorne,
S.Lovell,
K.P.Battaile,
X.Hu,
M.Shen,
S.D'Auria,
D.S.Auld.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In this work we characterize an alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) from the
hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrobaculum aerophilum (PyAeADHII). We have
previously found that PyAeADHII has no activity when standard ADH substrates are
used but is active when α-tetralone is used as substrate. Here, to gain
insights into enzyme function, we screened several chemical libraries for
enzymatic modulators using an assay employing α-tetralone. The results indicate
that PyAeADHII activity in the presence of α-tetralone was inhibited by
compounds such as flunarizine. We also examined metal coordination of the enzyme
in solution by performing metal substitution of the enzyme-bound zinc (Zn(2+))
with cobalt. The solution-based absorption spectra for cobalt substituted
PyAeADHII supports substitution at the structural Zn(2+) site. To gain
structural insight, we obtained the crystal structure of both wild-type and
cobalt-substituted PyAeADHII at 1.75 Å and 2.20 Å resolution, respectively.
The X-ray data confirmed one metal ion per monomer present only at the
structural site with otherwise close conservation to other ADH enzymes. We next
determined the co-crystal structure of the NADPH-bound form of the enzyme at
2.35 Å resolution to help define the active site region of the enzyme and this
data shows close structural conservation with horse ADH, despite the lack of a
catalytic Zn(2+) ion in PyAeADHII. Modeling of α-tetralone into the NADPH bound
structure suggests an arginine as a possible catalytic residue. The data
presented here can yield a better understanding of alcohol dehydrogenases
lacking the catalytic zinc as well as the structural features inherent to
thermostable enzymes.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

