 |
PDBsum entry 4j6t

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4j6t
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.18.1
- tyrosinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Melanin Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-tyrosine + O2 = L-dopaquinone + H2O
|
|
2.
|
2 L-dopa + O2 = 2 L-dopaquinone + 2 H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
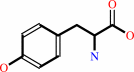 L-tyrosine
L-tyrosine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
L-dopaquinone
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
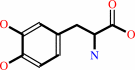 2
×
L-dopa
2
×
L-dopa
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
2
×
L-dopaquinone
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Cu cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Inorg Chem
18:895-903
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The mechanism of copper uptake by tyrosinase from Bacillus megaterium.
|
|
M.Kanteev,
M.Goldfeder,
M.Chojnacki,
N.Adir,
A.Fishman.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Tyrosinase belongs to the type 3 copper enzyme family, containing a dinuclear
copper center, CuA and CuB. It is mainly responsible for melanin production in a
wide range of organisms. Although copper ions are essential for the activity of
tyrosinase, the mechanism of copper uptake is still unclear. We have recently
determined the crystal structure of tyrosinase from Bacillus megaterium (TyrBm)
and revealed that this enzyme has tighter binding of CuA in comparison with CuB.
Investigating copper accumulation in TyrBm, we found that the presence of copper
has a more significant effect on the diphenolase activity. By decreasing the
concentration of copper, we increased the diphenolase to monophenolase activity
ratio twofold. Using a rational design approach, we identified five variants
having an impact on copper uptake. We have found that a major role of the highly
conserved Asn205 residue is to stabilize the orientation of the His204 imidazole
ring in the binding site, thereby promoting the correct coordination of CuB.
Further investigation of these variants revealed that Phe197, Met61, and Met184,
which are located at the entrance to the binding site, not only play a role in
copper uptake, but are also important for enhancing the diphenolase activity. We
propose a mechanism of copper accumulation by the enzyme as well as an approach
to changing the selectivity of TyrBm towards L-dopa production.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

